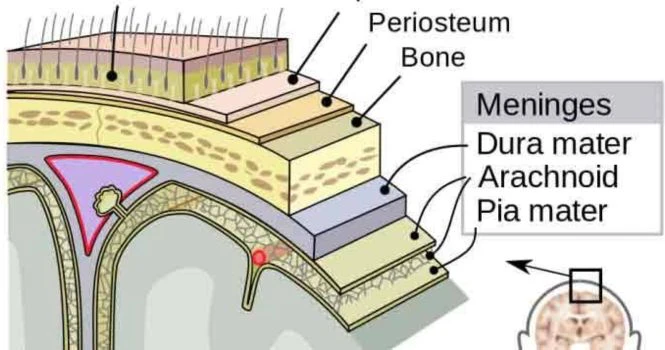
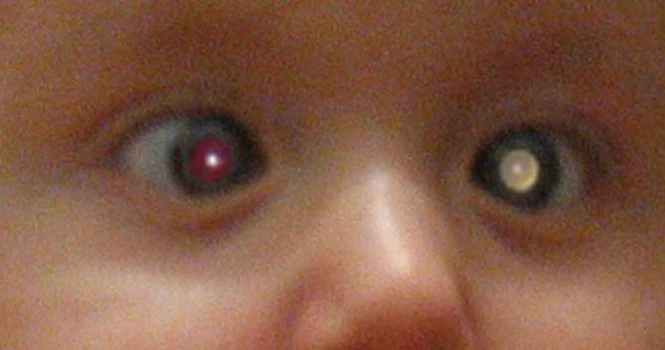
Meningitis is the infection of the covering of brain and spinal cord. It is most often caused by infection (Bacterial, viral, or fungal), but can also be produced by chemical irritation, subarachnoid haemorrhage, cancer and other conditions.
Usually suspected in any ill baby or child with poor feeding, unusual crying and vomiting. It is contagious and spreads by coughing, sneezing and thorough close contact.
It infects young adults and elders who has weakened immune system.
Viral meningitis is most common and does not cause serious illness. It is caused by a virus.
Bacterial meningitis can be fatal, if not treated early.
It is caused by bacteria.
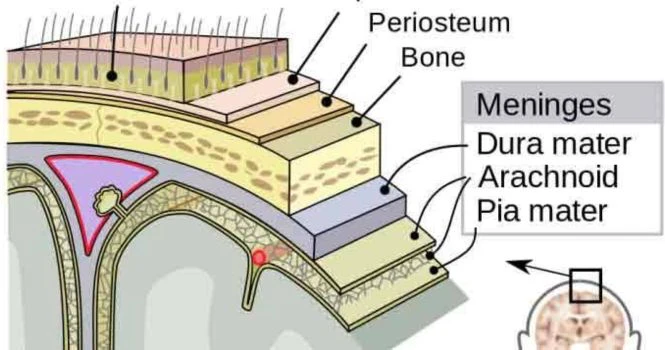
Transmission of Bacterial Meningitis:
The bacteria are transmitted from person-to-person through droplets of respiratory or throat secretions from carriers. Close and prolonged contact – such as kissing,sneezing or coughing on someone, or living in close quarters (such as a dormitory, sharing eating or drinking utensils) with an infected person (a carrier) – facilitates the spread of the disease.
The average incubation period is 4 days, but can range between 2 and 10 days.
Several bacteria can cause meningitis but the one one which infects and is a cause for large epidemics is Neisseria meningitidis. No animal reservoir is known and it only infects humans.
It is believed that 10% to 20% of the population carries Neisseria meningitidis in their throat at any given time. However, the carriage rate may be higher in epidemic situations.
Symptoms:
- A stiff and painful neck
- Fever
- Headache
- Vomiting
- Seizures
- Difficulty in staying awake
- Flu like symptoms like cough or troubled breathing
- Older adults might have mild headache or fever
Diagnosis of meningitis:
5% to 10% of patients die, even when the diagnosis is made early and treatment started with appropriate antibiotics. This emphasis, that more attention has to be given on immunisations as a preventive step towards this medical emergency.
Lumbar Puncture is the most important procedure for drawing CSF (Cerebrospinal fluid), to detect the organism which is causing the illness.
Bacterial Meningitis is treated in a hospital setting with antibiotics and you will be kept under observation to prevent serious problems like hearing loss, seizures or brain damage.
Talk to your doctor about immunization and ask if you or your child needs meningococcal vaccine, which is used to prevent bacterial meningitis.