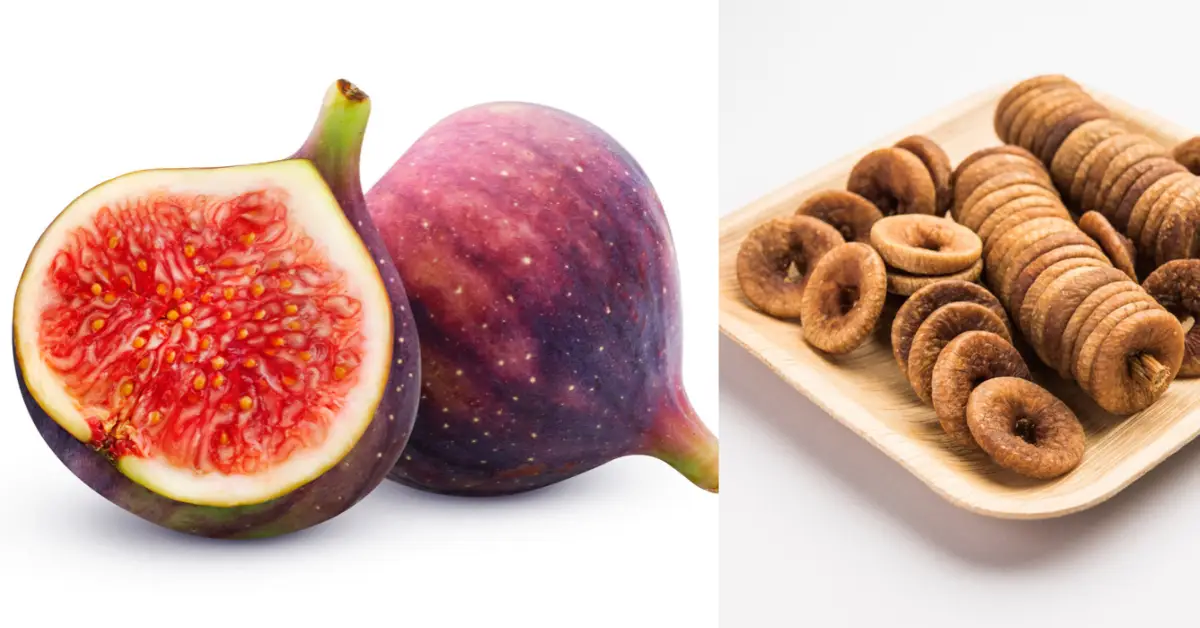
Anjeer, known as figs in English, is not just a fruit but a reservoir of nutrients and health benefits.
This ancient fruit, cherished for its sweet taste and chewy texture, is a staple in various cuisines and traditional medicines worldwide.
However, in the contemporary health-conscious world, understanding the glycemic index (GI) of foods, including anjeer, is crucial, especially for individuals managing blood sugar levels.
What is the Glycemic Index?
The glycemic index is a value used to measure how much specific foods increase blood sugar levels. Foods are ranked on a scale from 0 to 100, with pure glucose given a value of 100. Foods with a high GI are rapidly digested and absorbed, causing a quick spike in blood sugar levels, while those with a low GI have a slower digestion and absorption rate, leading to a gradual rise in blood sugar.
Anjeer Glycemic Index: A Closer Look
Anjeer, or figs, have a moderate glycemic index, generally ranging between 45 and 61. This places them in the low to moderate GI category, making them a relatively safe option for individuals looking to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
The fiber content in anjeer plays a pivotal role in its GI value. Dietary fiber slows down the digestion process, leading to a more gradual release of sugars into the bloodstream.
Health Benefits of Anjeer Beyond the Glycemic Index
Nutrient Density
Anjeer is packed with nutrients. It is an excellent source of dietary fiber, vitamins (A, B1, B2), minerals (potassium, magnesium, copper, iron), and antioxidants, making it a powerhouse of nutrition.
Digestive Health
The high fiber content in anjeer aids in healthy digestion and regular bowel movements, helping to prevent constipation and promote a healthy digestive system.
Heart Health
Anjeer’s fiber, potassium, and antioxidant content contribute to cardiovascular health by helping to lower blood pressure, reduce cholesterol levels, and prevent oxidative stress.
Weight Management
The fiber in anjeer also contributes to its role in weight management. It helps in feeling fuller for longer periods, reducing overall calorie intake, which can be beneficial for those trying to lose or manage their weight.
Bone Health
Rich in calcium and potassium, anjeer supports bone density and strength, playing a crucial role in maintaining long-term bone health.
Incorporating Anjeer into a Balanced Diet
Given its moderate GI and rich nutritional profile, anjeer can be a healthy addition to most diets. Here are some tips for including anjeer in your meals:
- Moderation is Key: Like any food, anjeer should be consumed in moderation, especially by those monitoring their blood sugar levels.
- Pairing with Low GI Foods: Pair anjeer with low GI foods like nuts or cheese to balance the meal and prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Hydration Matters: Dried anjeer (dried figs) is more concentrated in sugar and calories than fresh figs, so ensure you stay hydrated to aid in digestion and nutrient absorption.