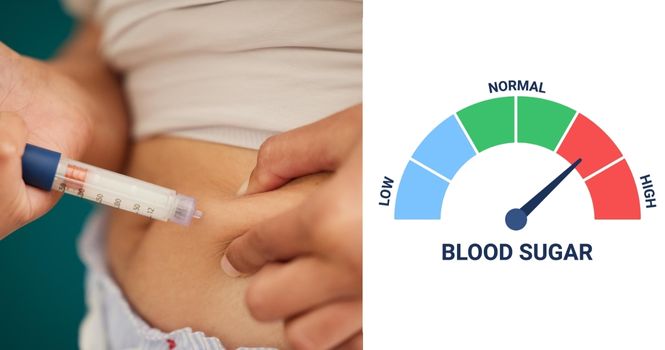
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, is a condition that primarily affects people with diabetes. It occurs when the body has too little insulin or when it cannot use insulin effectively.
Understanding High Glucose Symptoms is essential to manage the condition and prevent complications.
Let’s go through the signs and symptoms of hyperglycemia and how you can tackle this condition effectively.
What is Hyperglycemia?
Hyperglycemia is a hallmark feature of diabetes, but it can also occur in people with pre-diabetes or due to certain medical conditions. It happens when there is an excessive amount of glucose circulating in the blood plasma.
The American Diabetes Association notes that a fasting blood glucose level of 126 mg/dL or higher on two separate tests typically means a person has diabetes. Non-fasting glucose levels that are 200 mg/dL or higher can also indicate diabetes.
However, symptoms of hyperglycemia can start to appear when blood sugar levels are consistently above 180-200 mg/dL.
Extremely high blood sugar levels — like a 600 blood sugar reading — can lead to life-threatening complications if not managed promptly.
It’s important to remember that symptoms can vary from person to person and they may not always be present even if your blood sugar is high.
Recognizing the Symptoms of High Blood Sugar
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of high blood sugar is the first step towards managing hyperglycemia.
Here are some symptoms that may indicate your blood sugar is high:
1. Frequent urination:
When your blood sugar levels are high, your kidneys try to remove the excess glucose by filtering it out of the blood, which can lead to frequent urination.
2. Increased thirst:
Frequent urination can lead to increased thirst, another common symptom of hyperglycemia.
3. Fatigue:
High blood sugar can cause fatigue. The body’s cells cannot use glucose for energy effectively, leading to feelings of tiredness and exhaustion.
4. Blurred vision:
High blood sugar can cause the lens in the eye to swell, causing blurry vision.
5. Headaches:
Hyperglycemia can cause headaches and difficulty concentrating.
6. Slow-healing wounds:
High blood sugar levels can impair the body’s healing process and its ability to fight infections.
7. Unexplained weight loss:
Despite eating more than usual to relieve hunger, you may lose weight. Without the energy that glucose supplies, your body may begin to burn muscle and fat for energy instead.
Managing High Blood Sugar
If you experience symptoms of high blood sugar, it’s essential to consult your doctor. The following strategies can help manage hyperglycemia:
Monitoring blood sugar levels: Regular monitoring can help you understand how food, physical activity, and stress affect your blood sugar levels.
Healthy eating: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help maintain steady blood sugar levels.
Regular physical activity: Regular exercise can help lower your blood sugar level by moving sugar into your cells, where it’s used for energy.
Medication: If lifestyle changes are not enough, your doctor might prescribe medication or insulin to help manage your blood sugar levels.
Stress management: Stress hormones can cause your blood sugar levels to rise. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help manage stress and maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
Managing hyperglycemia involves recognizing its symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention.
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels according to age, leading a healthy lifestyle, and adherence to prescribed medication can go a long way in managing high blood sugar and preventing associated complications.
Always remember, every step taken towards a healthier lifestyle contributes to better blood sugar control.