Continuous Glucose monitoring is also called CGM or Ambulatory Glucose Profile.
It is a wearable technology, where it automatically measures the Blood Glucose Levels in real time, continuously all through the day.
There is a needle in the applicator which pushes the sensor just under the skin into the interstitial fluid (Fluid in between cells). You would feel a slight pinch
Glucometer measures Blood glucose from capillary blood and CGM means blood glucose from the interstitial fluid. Before taking any therapeutic decisions on the basis of CGM, consult your doctor.
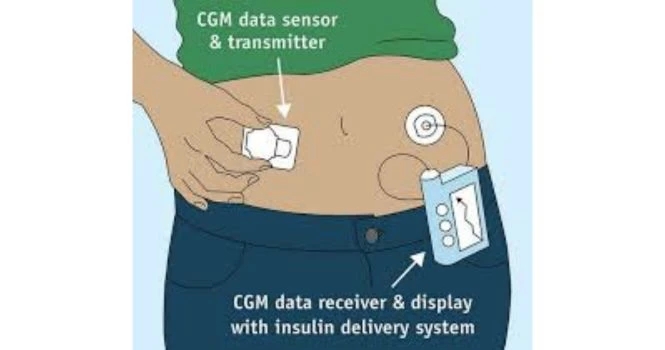
A small sensor is placed under the skin and it sends data to a transmitter that is worn on the body. The transmitter then sends the data to a receiver, which can be a smartphone, tablet, or special CGM device. The receiver displays the blood sugar data so that people can see their levels throughout the day.
Benefits of using Continuous Glucose Monitoring
- In patients where there is mismatch in Fasting, Post Prandial and HBA1c levels.
Patients who are in denial about the disease or those who don’t want to stop eating sweets or want to show their family members that their blood sugar is being maintained within normal limits, might strictly control it before visiting the doctor and if the doctor finds mismatch be Fasting and Post prandial and HbA1c levels, then might use CGM to know, how the blood sugar is maintained over 14 days.
- You don’t have to constantly check your blood sugar levels manually.
- The sensor can alert you if your blood sugar levels are getting too low or too high.
- Fluctuations in blood glucose can be known as the results are displayed in the graph, and it can help in adjustments to diet and medications as required.
- You can know which food , medicine or exercise type can result in an increase or decrease in Glucose levels and plan your diet and fitness routine accordingly.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring can help you avoid serious complications from diabetes, such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
- It can be used in Weight Loss management as well.
How are the CGM results interpreted?
It is interpreted by Time in Range
Time in range is the amount of time you spend in the target blood sugar (blood glucose) range—between 70 and 180 mg/dL for most people.
Who should use Time in Range in CGM Results?
People with type 1 diabetes and those with type 2 who are on insulin will benefit the most. Even people with type 2 diabetes can see how much time your glucose is in the range.
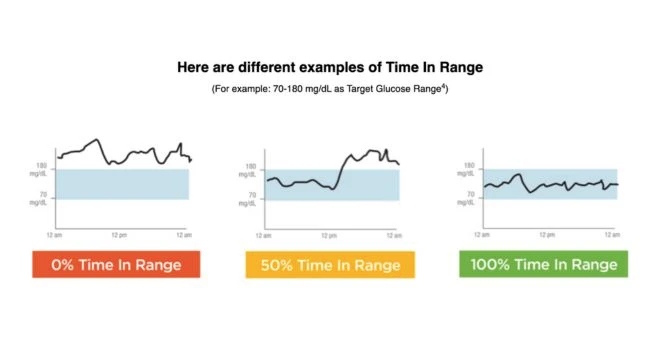
In this graph you can see the 0% in Range , 50% and 100% Target is to be at least 70% in Range.
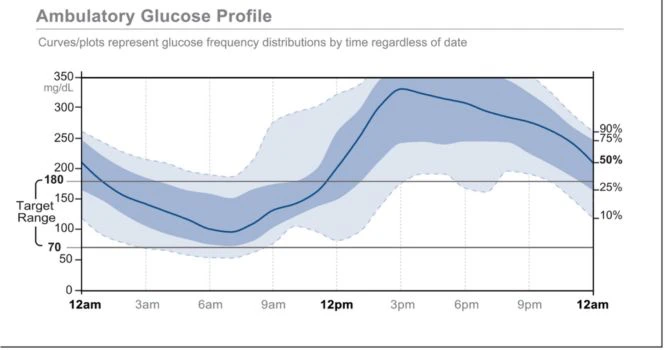
In the above graph you can see the Time in range is not under control.
Are Continuous Glucose Monitor and Insulin Pumps the same?
No, They are not.
- CGM devices measure your glucose level automatically every few minutes, all day long.
- Insulin pumps deliver a steady flow of insulin based on instructions you give.
Devices in market which help in Continuous Glucose Monitoring
There are many different Continuous Glucose Monitoring devices on the market.
Some of the most popular devices include the
- Cyborg Ultrahuman
- Dexcom G series,
- Medtronic Guardian system
- The Abbott Freestyle Libre.
These devices all have their own unique features, so it’s important to talk to your doctor or diabetes educator to find out which one is right for you.