GERD Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Let’s understand a few terms before we know about GERD or Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease.
HeartBurn
It is a feeling of burning sensation in the chest, behind the sternum, or the chest bone, often radiating to the neck.
Acid Reflux
It is a feeling of burning sensation in the chest, behind the sternum, or the chest bone, often radiating to the neck.
Definition of GERD
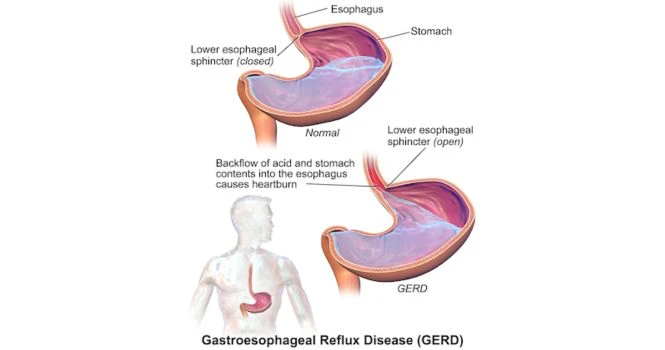
GERD or Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease is a condition which develops when reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus causes troublesome symptoms, which in turn may lead to complications.
Signs and Symptoms GERD
Regurgitation of sour material in the mouth and heartburn are the characteristic symptoms of GERD.
Most common symptoms are
- HeartBurn
- Regurgitation
Regurgitation is when reflux reaches the mouth. It may occur after meals or when you are asleep at night. It may even awaken you from sleep.
Other Symptoms are
- Dyspepsia ( Dyspepsia is recurrent pain or discomfort centered in the upper abdomen)
- Dysphagia (Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing)
- Belching (Belching is known commonly as Burping)
- Chest Pain
- Cough
- Hoarseness
Hoarseness is caused due to reflux laryngitis which is irritation in the back of the throat, caused due to acid reflux. The patient tends to keep on clearing the throat.
Population based studies have shown that 15% of the population have heartburn at least once a week and about 7% have heartburn everyday.
Most commonly, patients have mild disease and when acid from the stomach is being flowed back into the esophagus, it causes damage to the mucosa, causing ulcers in the lower part of the esophagus.
And around 1⁄3 of patients develop mucosal damage and it’s called Reflux Esophagitis.
If the reflux is severe, then it may reach the pharynx and mouth and can cause laryngitis, morning hoarseness and also cause breathing difficulty if it reaches the lungs.
Which Doctor to consult in GERD?
Ruling out cardiac causes of your symptoms is very important by your doctor who could be your Family Physician or Internal Medicine Doctor..
Are GERD and Gastritis the same?
In Gastritis the mucosa or the stomach lining is inflamed where as in GERD there is reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus.
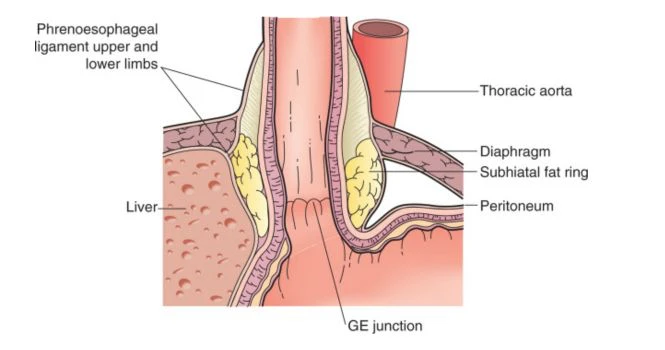
What causes GERD?
When we swallow food, the food passes through the food pipe and before entering the stomach, LES (Lower Esophageal Sphincter) relaxes, and food passes into the stomach.
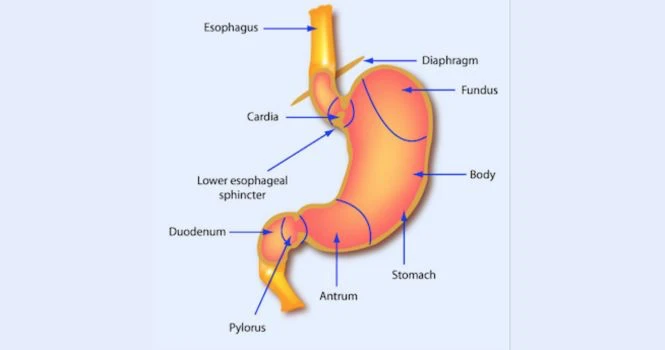
In GERD, LES relaxes in absence of swallowing or due to
- Loss of muscle tone in the Lower esophageal Sphincter, which acts as an internal sphincter.
- Incompetence of the diaphragmatic crural muscle, which acts as an external sphincter.
- The stomach contents are mostly likely to reflux,
- When Stomach volume is increases, which happens after meals
- When stomach contents are near the gastroesophageal junction, reflux happens when bending down, or when in a lying down position
- When Gastric pressure is increased, which happens when
- The person is Obese
- During Pregnancy
- When a person wears tight fitting clothes.
- Certain foods and medications, which relaxes the LES like fried or fatty food, citrus fruits etc
Which foods cause GERD?
Avoid the following, which relaxes the Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES sphincter), leading to Reflux
- Smoking
- Fried or Fatty food
- Tomatoes
- Spicy food
- Coffee
- Chocolates
- Mint
- Citrus fruits
- Large meals with fluids
How is GERD diagnosed?
Diagnostic studies are NOT required in the majority of patients with typical GERD symptoms.
Initially patients are treated with proton pump inhibitors drugs, which inhibit the secretion of acid from the stomach, for 4 to 8 weeks.
Majority of patients show improvement of their symptoms.
In Patients showing alarming features like,
- Troublesome Dysphagia (Difficulty while swallowing is called Troublesome Dysphagia. When it’s persistent, then the probability of peptic stricture or abnormal narrowing of passage, as the probable diagnosis increases but it usually happens after years of heartburn)
- Odynophagia (Pain while swallowing)
- Weight Loss
- Iron Deficiency Anemia
- Weight Loss
- Iron Deficiency Anemia
When patients show these alarming features then it warrants Upper Endoscopy to determine the type and extent of mucosal injury and to find out other conditions which mimic or resemble GERD and it’s complications.
Other investigation are,
Tests for GERD
Esophageal PH Monitoring to detect the amount of esophageal acid reflux.
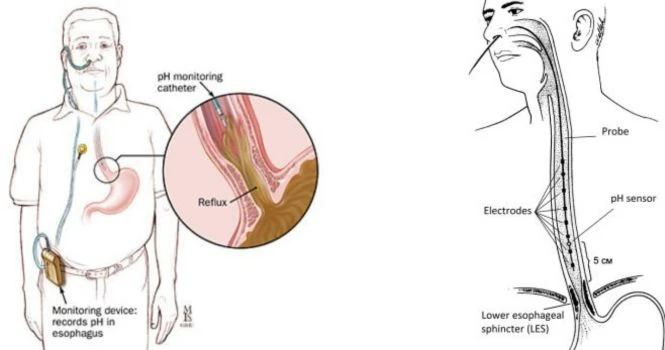
Combined esophageal 24 hour PH impedance Testing is for testing both acidic and non acidic reflux and to find the correlation between reflux events and symptoms, which is to understand if the reflux of stomach contents is causing the symptoms.
The Test involves placing a catheter, in the esophagus,by passing it through the nasal opening. The other end of the catheter is a data recorder machine.
You will be able to swallow, talk and breathe through the test procedure which is 24 hours.
These tests are NOT required for majority of patients but indicated in patients
- Typical symptoms, who are not responding to medications
- Atypical or extra esophageal symptoms
- Who are being considered for antireflux surgery.
Atypical or extra esophageal symptoms are
- Asthma,
- Chronic cough
- Laryngitis
- Chronic sore throat
Medications and Treatment for GERD
Managing GERD with Medicines
Aim of the treatment is
- Decrease Reflux
- Render Reflux Harmless
Mild Intermittent Symptoms(Uncomplicated Case)
Majority of the patients fall into this category, who have less than < 3 Episodes per week, mostly in response to precipitation factors.
When you have on and off symptoms, then Lifestyle Changes are advocated along with over the counter anti-secretory agents or antacids.
Changes to be incorporated are
- Weight Reduction, if overweight
- Sleep with Head-end Elevated. Not just the head, but the upper part of the body should be elevated.
- Don’t lie down immediately after food, be upright or walk for sometime.
- Have your last meal of the day at least 3 hours before you go to bed.
Moderate Cases
Moderate cases are 3 or more than 3 episodes per week. There could be Nocturnal awakening due to regurgitation. There might be Nocturnal choking.
Esophagitis may be present or absent.
Drugs like H2 receptor antagonist or H2 blockers like
- Cimetidine 200 mg
- Nizatidine 75 mg
- Famotidine 10 mg
are used, all of which are over the counter medications, whose dosages are, half of the prescribed limit, are prescribed for 6 to 12 weeks,for symptomatic relief.
NOTE: Ranitidine has been withdrawn by the US FDA after finding unacceptable levels of carcinogen.
These drugs, when taken during an active heartburn, take 30 minutes to act and can provide heartburn relief for 8 hours.
If the patient is resistant to the drugs or the drugs are not giving symptomatic relief then ,
Proton Pump inhibitors like
- Omeprazole
- Rabeprazole
- Pantoprazole
- Esomeprazole
are prescribed once a day for 8 weeks, taken 30 minutes before breakfast.
Approximately around 10 to 20% of patients do not get relief from once a day medications, so are prescribed twice a day, 30 minutes before breakfast and dinner.
Aim is to stop the acid which has a pH between 1 to 2 from causing damage.
Important to maintain the intragastric pH to 4 or more than 4, and if maintained for more than 18 hours / day, then it would help heal the mucosal damage, if any.
Proton pump inhibitors can help in acid suppression and are more effective in GERD.
Note: Vitamin B12 absorption is compromised.
Severe Cases
For patients with
● Typical symptoms, who are not responding to medications
● Atypical or extra esophageal symptoms
● Who are being considered for antireflux surgery.
Combined esophageal PH impedance testing is done. In resistant and complicated cases not responding to medical therapy, Surgery is advised, which is called Laparoscopic Fundoplication;

Where in gastric fundus is wrapped around the esophagus, which increases the LES pressure.
Complication of GERD
Malignancy is uncommon in the United states with 7000 cases per year. As GERD is a common condition, it doesn’t usually lead to cancer in short term and if the acid is irritating for longer duration of time , then the squamous cells in the lower esophagus turn into metaplastic columnar cells , leading to a condition known as Barett esophagus and this Barett esophagus
It is found in 15% of patients with Chronic Reflux. Having Barett esophagus increased the risk 11 times for cells showing dysplasia leading to cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are GERD and Heartburn the same thing?
Heartburn is a burning sensation in the chest while GERD is a condition caused due to reflux of stomach contents into esophagus causing heartburn and other symptoms.
2. Is Ginger Good for Acid Reflux?
No medical data suggests that it is good for reflux . But it is used in alleviating symptoms of nausea and vomiting .
3. Can GERD cause breathing problems?
Yes . If the reflux enters the lungs, then it may cause pulmonary aspiration and asthma, leading to breathing problems.
4. Can GERD cause weight loss?
Yes. It is possible. We have seen GERD causing dIfficulty in swallowing and this may lead the patient to not have proper nutrition, leading to weight loss.
Sources
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15986857/
BruceBlaus, CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0,, via Wikimedia Commons
BruceBlaus, CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
LittleT889, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
![]()