Small Pox(Variola) and Chicken Pox(Varicella)
What is Small Pox?
Small Pox is caused by Variola Virus.It was officially eradicated in 1979.Before being eradicated, It killed millions of people.
30 out of every 100 person who were infected, died.
Transmission of small Pox
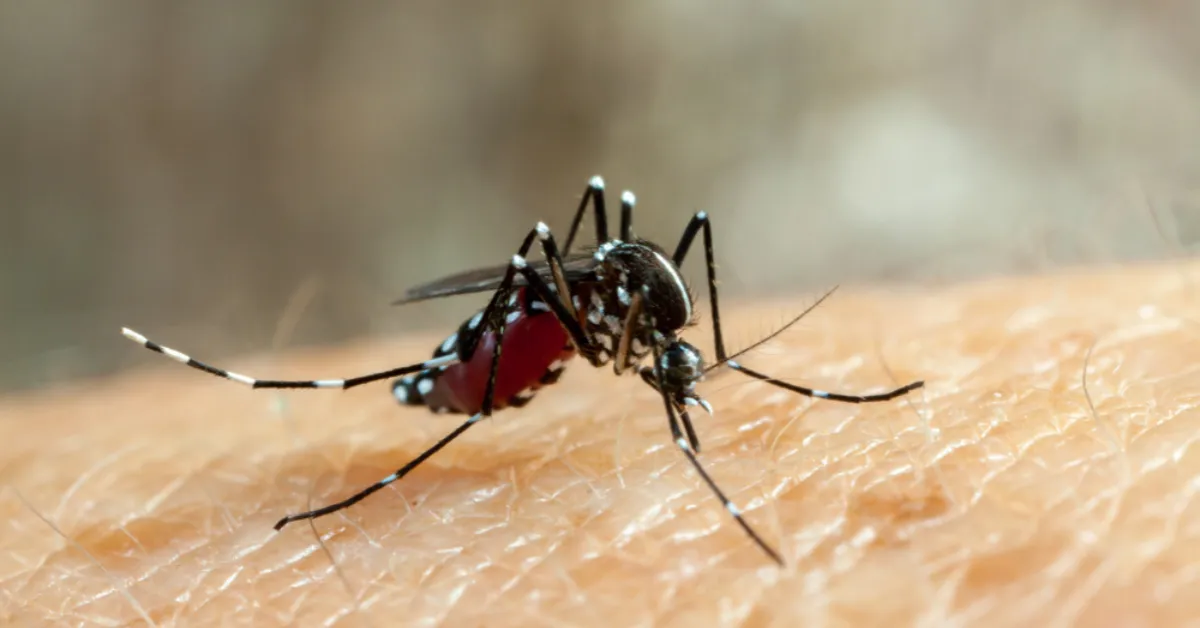
Spread by droplets released in air, when any infected person sneezes, talks and coughs. Its enters through the respiratory tract.
Is Small Pox Vaccine Available now anywhere in the world?
Its Available only with World Health Organisation,which has a reserve stock, to tackle any emergencies which might arise and have the capacity to protect 200 million people.
Routine small Pox vaccination was stopped in USA in 1972.
Last case reported in India was on 24 th May 1975 and India was declared small Pox free on 5 th July, 1975.
The World Health assembly declared Global Eradication of Small Pox in may 1980.
What is Chicken Pox?
Chicken Pox is acute, highly infectious disease caused by Varicella-Zoster Virus.
Also called, VZ Virus or Human(alpha)Herpes Virus 3
It normally occurs in children less than 10 years and in adults who weren’t infected in childhood, the disease is more severe in adulthood.
One attack gives durable immunity and second attacks are rare but have been reported.
Infection with Varicella Virus causes Chicken Pox, when it resolves completely, the virus is not eliminated from the body but commonly establishes latent infection, which means the person has the virus but doesn’t exhibit any clinical manifestation of the disease.
The sites where the virus resides in human are the cranial nerves, dorsal nerve root ganglia often for decades without exhibiting any signs and symptoms. The Virus may reactivate and cause Herpes Zoster in 30% of individuals during immune suppressive therapy and as one gets older, due to waning of Cell-Mediated Immunity.
Incubation period of Chicken Pox:
Incubation period is usually 14-16 Days but 10-21 days have also been reported.
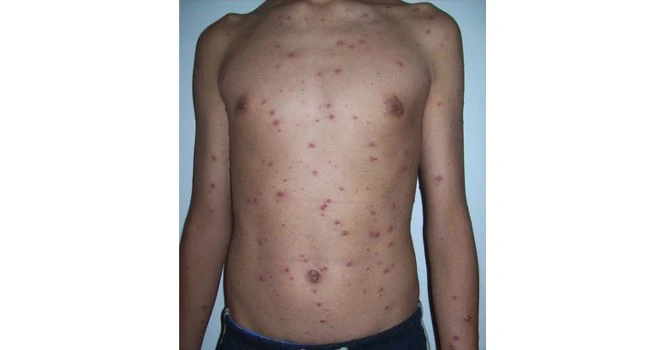
Signs and Symptoms of Chicken Pox
- Painful, Vesicular(A small fluid-filled sac) and pustular[A pustule is a small collection of pus in the top layer of skin (epidermis) or beneath it in the dermis] eruption.
- Located centripetally (usually in the centre of the body on abdomen)
- Rash mostly on Flexor Surfaces with severe itching
- Loss of Appeitite
- Tiredness
- Axilla(under arms) are involved.
- Palms and soles are rarely affected.
- Dew Drop like appearance.
- Different stages of rash evident in one particular time.
- Area of inflammation seen around the vesicles.
- Evolution of rash is very rapid.
- Scabs begin to form within 4-7 days after rash appears.
- Temperature rises with each fresh crop of rash.
Transmission of Chicken Pox:
Spread by droplets released in air, when any infected person sneezes, talks and coughs. Its port of entry into the human body is through upper respiratory tract and conjunctiva.
The source of infection is usually a case of Chicken Pox.
Scabs are non infective.
Chicken Pox during Pregnancy
If a Pregnant Woman is infected, the virus can cross the placental barrier and infect the fetus, a condition called Congenital Varicella. Consult your doctor for further guidance and treatment.
Prevention:
1. Varicella Zoster Immunoglobulin(VZIG):
Recommended to be given within 72 hours of exposure to virus particularly in immunosuppressed individuals.
2. A Live Attenuated Varicella Virus Vaccine:
It is recommended in children 12 to 18 months who have not had Chicken Pox.
Treatment of Chicken Pox:
Anti-Viral medications are given by your doctor.
Calamine lotion can be applied to relieve itching.
Do not use aspirin or aspirin-containing products to relieve fever from chickenpox. The use of aspirin in children with chickenpox has been associated with Reye’s syndrome, a severe disease that affects the liver and brain and can cause death.
Related Viral Disease: Measles
Another highly contagious viral disease is Measles, caused by the Measles virus from the Paramyxovirus family. Like Chicken Pox and Small Pox, it spreads through droplets in the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Measles often begins with fever, cough, runny nose, and red eyes, followed by a widespread rash.
Although Measles can lead to serious complications such as pneumonia, brain swelling (encephalitis), and even death, it is entirely preventable through vaccination.
👉 Read more about measles symptoms, prevention, and outbreaks here.
Sources
References:
1. http://www.who.int/csr/disease/smallpox/faq/en/
2. WHO (1980) The Global eradication of Small Pox, Final Report ,Geneva
3. https://www.cdc.gov/chickenpox/
4. https://www.cdc.gov/chickenpox/about/prevention-treatment.html
Image :
1. chicken pox rash in child face : By Øyvind Holmstad (Own work) [CC BY-SA 4.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
2. By Camiloaranzales (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
![]()