Tuberculosis or TB

Synonyms: TB, Pulmonary Tuberculosis, Latent Tuberculosis.
Definition:
Tuberculosis is caused by a bacteria, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, spread from person to person by droplets dispersed in air when patients coughs, sneezes, speaks or sings.
Normally, when bacteria invades, the type of cell which engulfs and kills the bacteria are macrophages. But the TB bacteria, Mycobacterium tuberculosis has the capacity to survive within macrophages,which is a cause for burden of disease in the world.
Prevalence of TB:
A total of 9,557 TB cases (a rate of 3.0 cases per 100,000 persons) were reported in the United States in 2015.
In 2014 it was 9406 TB cases.
Rates of TB for Different Racial and Ethnic Groups
For this report, persons identified as white, black, Asian, American Indian/Alaska Native, native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander, or of multiple races are all non-Hispanic. Persons identified as Hispanic may be of any race.
- American Indians or Alaska Natives: 6.1 TB cases per 100,000 persons
- Asians: 18.2 TB cases per 100,000 persons
- Blacks or African Americans: 5.0 TB cases per 100,000 persons
- Native Hawaiians and other Pacific Islanders: 18.2 TB cases per 100,000 persons
- Hispanics or Latinos: 4.8 TB cases per 100,000 persons
- Whites: 0.6 TB cases per 100,000 persons
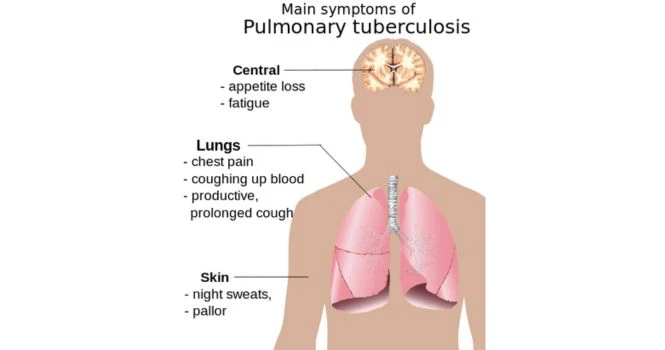
Signs and Symptoms of Tuberculosis
1. Patient having persistent cough for more than 15 days,
2. Pain in the chest
2. Blood in sputum
3. Weakness and fatigue
4. Loss of weight
5. Reduced appetite
6. Evening temperature
How is TB transmitted from person to person?
If a patient with active TB coughs, sneezes, speaks or sings, then the droplets released from mouth may harbour the bacilli, and the air , if breathed by a person nearby, then he gets infected.
We see doctors wearing face masks to prevent themselves from being infected and also we see patients, with active TB in hospital wards wearing it as well,so as not to spread it to others.
Is Tuberculosis transmitted by Kissing?
Tuberculosis may be transmitted during the act of kissing if the person kissing is an open case of tuberculosis excreting large numbers of mycobacteria in the sputum. As the droplets dispersed in air are very small are also being suspended in air for longer duration.
Lack of awareness and suspected individuals at high risk not being tested, is giving rise to the burden of disease in the community.
TB is NOT spread by
– Handshake
– Sharing food or drink
– Touching bed linens or toilet seats
– Sharing toothbrushes
What is Latent Tuberculosis?
A person has latent TB, when the bacilli, Mycobacterium tuberculosis is alive inside the macrophages but Inactive and doesn’t exhibit any signs and symptoms and the patient cannot transmit the bacilli. 5 to 10% of them would eventually develop TB, due to reactivation of the dormant bacilli. Even Latent TB must be treated.
What is Pulmonary Tuberculosis?
TB Bacilli usually grow in the lungs, hence called pulmonary Tuberculosis. If its affects other parts, other than lungs, then its called extra-pulmonary Tuberculosis. It is known to affect Bone, lymph nodes, pleura, meninges, urinary tract, kidney.

Diagnosis of Tuberculosis
Who should take the TB Test?
- If you have been with the person who was diagnosed with TB.
- If you are in a country where TB prevalence is high(Latin America, the Caribbean, Africa, Asia, Eastern Europe, and Russia).
- Infants, children and adolescents who are in close proximity with adults who are at increased risk of latent TB.
- People working in high risk settings, like nursing homes, hospitals, home-care shelters.
Following are at high risk for developing TB,
1. Patients who are HIV Positive
2. Patients who have co-morbid diseases which weaken immune system
3. Babies and young children along with elderly.
What are the tests to diagnose Tuberculosis?
1. Sputum Test
2. Skin Test
3. Blood Test
Sputum test is the most important laboratory test for pulmonary tuberculosis. While giving the sample for sputum testing, Remember to go to an open air space with no one around and then cough to collect atleast 5 ml of muco-purulent sputum.
(Muco-Purulent means composed of or containing both mucus and pus)
In children less than 2 years who tend to swallow sputum, gastric aspirate is preferred sample.
Patients with Latent Tuberculosis, will not excrete bacilli in the sputum, so the test is of no use in them.
Chest X-Ray is screening Test and not a Confirmatory test.
2) Skin Test for TB
Tuberculin Test or Mantoux test:
0.1 ml of purified protein derivative is injected under the skin in front of forearm, and the result read after 48 to 72 hours.
Transverse Induration must be measured in mm. Redness is NOT measured. An Induration of 5 mm or more is considered positive for TB infection and other factors which might influence the induration are prior infection with HIV and other factors.
Persons immunised with BCG may give false Positive result.
Tests for latent TB :
1) Mantoux or Tuberculin Test
2) IGRA Test ( TB GOLD) Interferon Gamma Release Assay
Both the above tests cannot differentiate between active TB and Latent TB, so must be used for screening. Not recommended for active TB detection.
Specimen for Latent TB includes blood samples along with identification of individuals who are at increased risk of development of active TB (close contacts of active TB cases)
What are the drugs used to treat TB?
1. Isoniazid
2. Rifampicin
3. Pyrazinamide
4. Streptomycin
5. Ethambutol
6. Thioacetazone
Your doctor would prescribe drugs in combination, taking into account lot of factors including side effects of these drugs.
Please complete the course till the last day and last tablet as directed by your physician, and if we don’t complete the full course, then the bacilli will not be killed completely and it gives rise to relapses and drug resistant strains.
Adverse effects during TB therapy
The side effects listed below are serious. If you have any of these symptoms, call your doctor or nurse immediately:
- No appetite
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Yellowish skin or eyes
- Fever for 3 or more days
- Abdominal pain
- Tingling in the fingers or toes
- Pain in the lower chest or heart burn
- Feeling itchy
- Skin rash
- Easy bruising
- Bleeding from gums
- Nose bleeding
- Urine becomes dark or brown in color
- Aching joints
- Dizziness
- Tingling or numbness around the mouth
- Blurred or changed vision
- Ringing in the ears
- Hearing loss
The side effects listed below are minor problems. If you have any of these side effects, you can continue taking your medicine.
Rifampin can turn urine, saliva, or tears orange. The doctor or nurse may advise you not to wear soft contact lenses because they may get stained.
Rifampin can make you more sensitive to the sun. This means you should use a good sunscreen and cover exposed areas so you don’t burn.
Rifampin makes birth control pills and implants less effective. Women who take rifampin should use another form of birth control.
If you are taking rifampin as well as methadone (used to treat drug addiction), you may have withdrawal symptoms. Your doctor or nurse may need to adjust your methadone dosage.
Is TB curable?
YES, it is curable if the patient completes the full course of prescribed medicines. Even though you feel completely well, do not stop the TB medications, as the bacilli would not be killed, until you complete the full course.
Vaccination for Tuberculosis
World Health Organisation has recommended the , Danish 1331 Strain for production of BCG Vaccine.
BCG Stands for Bacilli Calmette Guerin.
Age of administration is at Birth or at 6 weeks of age
Dosage is 0.1 mg in 0.1 ml Volumem(Dose for new born children
below 4 weeks is 0.05 ml)
Site of injection: Just above the insertion of deltoid muscle Route of Administration : Intradermal with tuberculin syringe
Diluent Used : Normal Saline
Storage of vaccine: Wrapped in double layer of red or black cloth.
Contraindications to BCG Vaccine:
Unless specifically indicated, BCG should not be given to patients suffering from,
1. Generalised Eczema
2. Infective Dermatosis
3. Hypogammaglobulinaema
4. Patient with history of deficient immunity.
TB in children
Signs and Symptoms of childhood TB include,
- Chronic Fever
- Cough
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Failure to gain weight
- Lymph node enlargement.
While it remains a challenge to diagnose Childhood Tuberculosis, as NO single test works well in childhood TB.
Its relied on the combination of clinical features and lab tests, which are
1. History of contact with Adult with TB
2. Any symptom suggestive of TB
3. Mantoux Test or Interferon-gamma release assay: Positive tests is an evidence of TB infection
4. Chest X-Ray
5. Smear Microscopy
6. GeneXpert
7. Liquid Cultures
IF the above combination of above fails then the patient must be treated empirically and assess clinical response.
TB and HIV
In 2013, 13% of all cases of TB occurred in people living with HIV (PLWH).
The rate of new TB disease diagnoses in 2013 was 3.0 per 100,000 population (9,582 cases), the lowest since reporting began in 1953. Its slightly increased in 2014 and 2015.
HIV infection is one of the strongest risk factor for progression from Latent TB to active TB. To stay informed about recent case spikes and emerging trends, read our latest update on the 2025 Tuberculosis Outbreak.
All patients who are diagnosed with active TB must be tested for HIV
Counseling for TB Patients
From the time of diagnosis to completion of the full course of prescribed one requires to be mentally strong too as the duration of treatment is long.
For those affected by this disease, its something deeply personal. Family support and understanding about the disease is very important.
Patients need to be away from office and visiting friends and need to take medications for few weeks before they are not infective. Ask your doctor about when to resume normal activities.
Adherence to TB treatment is Vital.
Patients would be worried about transferring the infection to immediate family members.
Psychological distress such as depression and other mental co-morbidities have often been associated with TB and rates of mental illness reaching as high as 70% among TB patients.
Patients must be counselled on the importance of completing full course of medications prescribed and also be told about the resistance to drugs, if stopped abruptly and re-emergence of the infection later on, which is giving rise to Multi Drug Resistant Tuberculosis.
Patients along with family members must be counselled at every opportunity and physical , financial and psycho-social and nutritional needs must be addressed.
Sources
References:
1) IPAQT : Initiative for Promoting affordable and Quality TB Tests
2) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. USA.
3)Dr. S. Parija
Head of Department of Microbiology, JIPMER, Pondicherry in interview with NDTV.
4) Doherty AM et al. A review of interplay between tuberculosis and mental health Gen Hospital Psychiatry 2013;35(4):398-406.
Images:
1.Pulmonary TB: By Mikael Häggström (All used images are in public domain.) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
2.Extra Pulmonary TB :By James Gathany (CDC Public Health Image library ID 11162) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
![]()