Dizziness is a troublesome symptom to have, often scary and everything comes to a standstill, when our head is spinning and we reach out to nearby things to hold on for support.
Dizziness also commonly referred by different names according to how the patients feel, such as
- Giddiness
- Lightheadedness
- Head spinning
- Mental confusion
- Blurred vision
Patients may feel dizzy due to a lot of reasons; BUT if there is sudden dizziness, loss of balance or coordination and trouble walking, which happen to be warning signs of a STROKE, which is a Medical emergency. It’s important to go to the Hospital, to rule out any serious conditions which require immediate attention.
Which Doctor Would You Consult for Dizziness?
You could consult a
- Neurologist
- Otorhinolaryngologist , commonly called the ENT doctor
- Family Physician.
They would guide to any cross references to any specialty , if required.
To overcome the challenge of coming to a diagnosis, your doctor would ask you to give a detailed medical history to come to a probable cause and then chart out a treatment plan accordingly.
Evaluating Dizziness Problem
When a patient complains of dizziness, then a medical history is important as the term “dizziness” is described by patients differently. Some describe it as mental confusion, blurred vision; then there are Patients who complain of Dizziness while walking. These are Gait or walking disorders.
After ruling out misleading symptoms and walking/Gait disorders, Dizziness can be classified as
- Presyncope ( Faintness)
- Vertigo
- Miscellaneous Head Sensations
Presyncope is a feeling that the person feels before an episode of fainting.
Vertigo, is the feeling of Head spinning sensation. It’s also described as the sensation of motion when there is no motion or when there is a small movement, the feeling of an exaggerated sense of motion in response to that small movement. It may be accompanied by nausea or vomiting.
To keep the body posture steady; 3 Body systems come into play,
- Vestibular system ( in the inner ear )
- Eyes
- Somatosensory system (Muscle, joints and Skin)
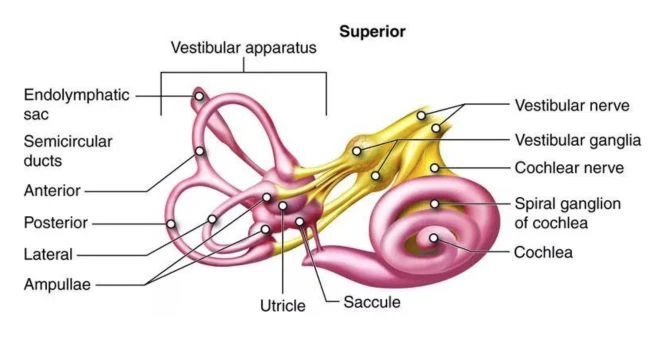
The inner ear, the eyes along with that somatosensory system, like the joints and muscle send signals to the brain to keep the posture steady.
These act in sync and help each other to keep the person upright and steady at rest and in motion. If one is lacking, the other compensates to make sure the person’s posture is stable and steady.
Causes of Dizziness or Head Spinning Reasons
Vertigo could be a symptom of many underlying conditions.
To know the cause, we must differentiate between the Central cause of Vertigo from the Peripheral Cause.
In Central Cause, Brain is involved and Onset is gradual or slow, without any Ear symptoms.
In Peripheral Cause, the Onset is sudden, often with associated ear symptoms, like ringing in the ears and loss of hearing.
There could be involvement of both the central and Peripheral causes.
The central causes of Vertigo are,
- Head Injury
- Seizures
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Cerebellar Ataxia Symptoms
- Wernicke encephalopathy
- Chiari Malformations
The Peripheral causes of Vertigo are more common , which include
- Vestibular neuritis or Labyrinthitis
- Meniere’s Disease
- Benign Paroxysmal Positioning Vertigo or BPPV
- Alcohol intoxication
- Trauma to inner ear
- Semicircular canal dehiscence
Combined Central and Peripheral Causes of Vertigo include,
- Stroke
- Migraine
- Endocrinopathies
- Hypothyroidism
- Pendred Syndrome
- Infections
- Lyme Disease
- Syphilis
- Cerebellopontine angle tumors
- Vestibular schwannoma
- Meningioma
- COVID 19
- Hyperviscosity syndromes
- Waldenström macroglobulinemia
8. Vascular compression
The above reasons are exhaustive and all of them cause the symptom, but it could be as simple as any school going children feeling dizzy and faint during a school assembly, which could be due to skipping breakfast or due to exercise during morning assembly. This may be due to overexertion or dehydration.
And when there is dizziness in a middle aged person, when they change the position of the head, either while rolling over in the bed, or when they look upwards or while bending down; Then it leads to Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. BPPV.
Other cause could be Migraine Headache in Women,
Or if you have an Ear infection, it could be Labyrinthitis, which is an inner ear infection which is affecting the balance.
Or if you are Pregnant
Or due to Low Blood sugar
Or due to some medications which you might be taking.
Dizziness is also associated with Heart conditions like Tachy Brady Syndrome, where the SA node in the heart, which triggers the neural impulses for the heart to contract, is defective.
Other probable causes for Dizziness could be ,
- Hypotension or Low Blood Pressure
- Anemia
- Allergies
- Motion sickness
- Heat stroke
- Anxiety
- Medications
With so many Causes, there is a tendency for the diagnosis to be missed, therefore thorough evaluation has to be done by the Doctor and then treatment planned accordingly. The following test studies help distinguish between central and peripheral lesions and identify causes requiring specific therapy
The Following Lab Tests are indicated in patients with persistent vertigo or when CNS disease is suspected.
Laboratory investigations in Dizziness
- Audiologic evaluation,
- Caloric stimulation,
- ENG or Electronystagmography
- VNG or Videonystagmography
- Vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials (VEMPs), and
- MRI
Some patients have normal neurological and vestibular function Tests, and then, Dizziness is caused due to,
- Hyperventilation syndrome
- Hypoglycemia
- Somatic symptoms of Clinical Depression
Let’s know about the most common cause of Dizziness which are reported in our OPD OutPatient Department happens to be;
Benign Paroxysmal Positioning Vertigo or BPPV
- Benign
- Paroxysmal
- Positional
- Vertigo
Benign, which means, not harmful
Paroxysmal means sudden increase or recurrence of symptoms
Positioning Vertigo, meaning vertigo caused due to position of the head.
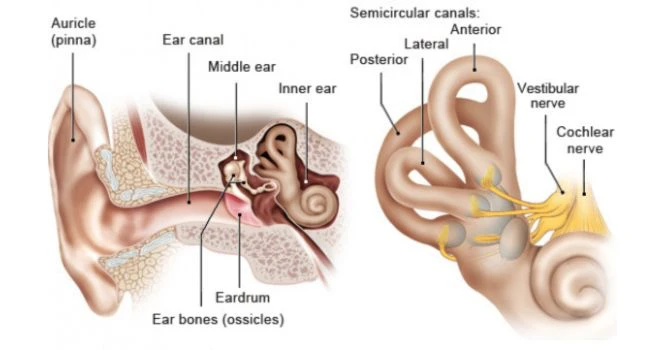
We have seen that, in Vertigo there is a feeling of sensation of motion when there is no motion or When there is a small movement, the feeling of an exaggerated sense of motion in response to that small movement.
In BPPV, patients suffer recurrent spells of vertigo, often provoked by rolling over in bed.
There is a brief latency period or delay of 10 to 15 seconds, before the symptoms develop.
That means, when the patient rolls over in bed, the symptoms appear after a few seconds, after the head is moved. And the acute Vertigo subsides within 10 to 60 seconds, though the patient may remain imbalanced for several hours.
It’s important to remember that such brief latency or delay is not seen in central lesions (Conditions involving the brain).
In central lesions, there is no latent period, fatigability, or habituation of the symptoms and signs. That’s why MRI is asked to rule out CNS disorders.
The symptoms in BPPV, persist for several days and even though it’s NOT a serious condition; it’s a very unpleasant symptom to have, as there is fear in the patient about the loss of balance momentarily, holding on to nearby things for support, and the patient is left confused and not knowing why it happened or what to do next .
The Symptoms tend to appear,
- When you look upwards
- When you lie down in bed on the back, after a few seconds,you suddenly feel dizzy,
- Or when you bend downwards
The patient may be without any symptoms, when driving the car, as long as the position of the head is stable. BUT remember it’s dangerous to drive, until you are free from symptoms.
Causes of Benign Paroxysmal Positioning Vertigo BPPV
It may be due to Head Trauma or due to free flowing otoconia in the semicircular canals.
Our ear is essential to our sense of Balance and it is maintained by the vestibular system found in the inner ear.
It is made up of semicircular canals and 2 otolith organs, namely, Utricle and Saccule.
Both semicircular and Utricle and Saccule, have thin sensory hair cells. But in Utricle and Saccule, these sensory hair tips have small crystals on them.
These crystals are called otoliths or ear rocks. The otolith organs detect acceleration, for instance when you take an elevator, or fall down, or pick up speed in a car.
These crystals are made up of Calcium carbonate crystals or otoconia.
It is theorised that, When these crystals get dislodged due to injury, infection or age, they tend to get dissolved in the Utricle. But before being dissolved, when the patient moves his or her head, then these crystals or particles tend to stimulate the hair like cells or cilia in the semicircular canals, which causes this sensation.
If it happens recurrently then your doc would advise MRI to rule out Central Nervous System disorders.
Treatment of BPPV
Treatment is aimed at removing the free floating otoconia from the semicircular canals by physical therapy protocols (eg, the Epley maneuver or Brandt-Daroff exercises)
The most common location where the crystals are found is the posterior semicircular canal. SO the Maneuver helps to move the crystals out of the semicircular canals and relieve symptoms.
Even without treatment, It usually goes away in days or weeks. Keep yourself well hydrated.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can dizziness be a sign of eye problems?
Yes. It may be due to eyes problems such as
- Incorrect glasses
- Binocular vision disorder
- Traumatic injury to brain
- Eye Strain
Or anything which causes disruption in the signals from eye to brain, causes Dizziness.
2. Can dizziness be a symptom of a stroke?
Yes. It could be a symptom of Stroke. Read the following signs carefully and understand the signs to look out for ,
F.A.S.T. Warning Signs
Use the letters in F.A.S.T to spot a Stroke
F = Face Drooping :
- Does one side of the face droop or is it numb?
- Ask the person to smile. Is the person’s smile uneven?
A = Arm Weakness :
- Is one arm weak or numb?
- Ask the person to raise both arms. Does one arm drift downward?
S = Speech Difficulty :
- Is speech slurred?
T = Time to call 911 in USA (Your Local Emergency Number)
Other Stroke Symptoms
Watch for Sudden:
- NUMBNESS or weakness of face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body
- CONFUSION, trouble speaking or understanding speech
- TROUBLE SEEING in one or both eyes
- TROUBLE WALKING, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
- SEVERE HEADACHE with no known cause