Carbohydrates And Its Sources
Carbohydrates : Definition, Types, Structure | Carbohydrate Food List | Good Carbs and Bad Carbs
Carbohydrates Definition :
Carbohydrates, composed of Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in their chemical structure are an essential source of energy for the human body.
Carbohydrates general formula is Cx(H2O)n
Glucose formula is C6H12O6
Carbohydrates Classification and Types
Carbohydrates which we find in our daily foods are divided into
- Monosaccharides
- Disaccharides
- Oligosaccharides
- Polysaccharides
Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides are made up of one sugar unit . They are called simple sugars.
Mono means “One” and Saccharides is derived from greek word, sákkharon, which means Sugar. In Hindi language it’s called, “Sahkkar”
The Chemical structure of Monosaccharide is displayed

Examples of Monosaccharides are
- Glucose
- Galactose
- Fructose
Few examples of Monosaccharides , in everyday life are,
- Fresh Fruits
- Jams
- Breakfast Cereals
- Honey
- Sweet Corn
- Pasta Sauces
- Instant Coffee Granules Etc
Disaccharides
Di means, “Two” . Disaccharides are made up of 2 Monosaccharide Units linked together
The Chemical structure of Disaccharide is displayed

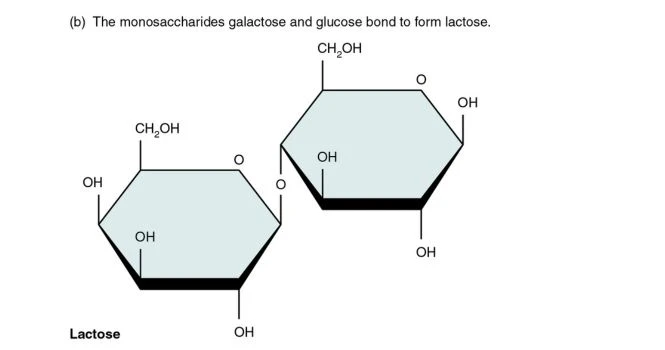

Examples of Disaccharides are
- Sucrose
- Lactose
- Maltose
Few examples of Disaccharides , in everyday life are,
- Table sugar
- Cakes Cookies and Dark Chocolate
- Beetroot and Carrots
- Bread
- Breakfast cereals
- Beer
- Milk and Milk Products including ice-creams
Oligosaccharides
These are made up of 3 to 9 Monosaccharide units linked together
Examples of Oligosaccharides are
- Raffinose
- Inulin
- Stachyose
Few examples of Oligosaccharides , in everyday life are,
- Legumes
- Beans
- Cabbage
- Broccoli
- Onion
- Fennel
- Asparagus
Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides are made up of 10 or more Monosaccharide Units linked together in different ways.
Examples of Polysaccharides are Starch , Glycogen and Cellulose .
The Chemical structure of Polysaccharide is displayed
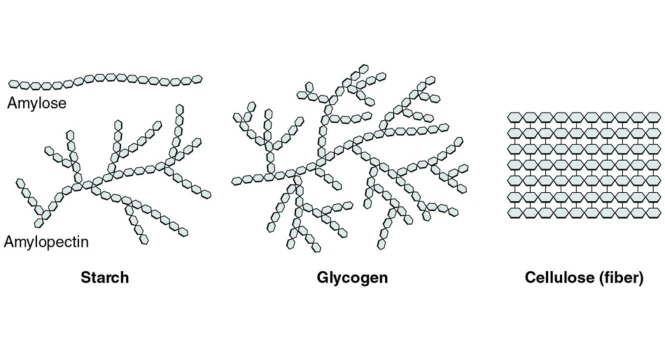
Few examples of Polysaccharides , in everyday life are,
- Starch Polysaccharides
- Non Starchy Polysaccharides
Examples of Starchy foods
- Rice
- Oats
- Instant Noodles
- Potato
Examples of Non Starchy Foods
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Whole grain Cereals
- Pulses
Now that we have seen the classification and types of Carbohydrates or Carbs are we commonly call it , lets see
How and Where Carbohydrates are Digested?
Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth , as in when you eat cooked starch like Rice or Oats, saliva helps in the digestion with an enzyme salivary amylase, converting a small portion of it into disaccharide, while the bolus of food moves into stomach.
In Stomach, there is gastric juice, whose action is negligible
Then there is action of an enzyme Pancreatic Amylase, present in the pancreatic juice, which converts it into dextrin, Maltose and maltotriose.
In Small Intestine, where succus entericus is secreted and
- Along with enzyme sucrase converts sucrose into Glucose and Fructose and
- Along with enzyme Maltase converts Maltose and Maltotriose into Glucose
- Along with enzyme Lactase converts Lactose into Glucose and Galactose
- Along with enzyme Dextrinase converts Dextrin, maltose and maltotriose into Glucose
- Along with enzyme Trehalase converts Trehalose into Glucose.
Note : Succus Entericus is secreted in the small intestine, which is alkaline , to neutralise the acidic nature of the food content from the stomach, which is about to enter the small intestine.
Finally the end product of Carbohydrate Digestion is GLUCOSE. Glucose represents 80% of the final end product of digestion and another 20% is of fructose and galactose.
So this Glucose is used as the energy source for our body, providing 4 Calories per gram of carbohydrate.
So when Glucose is the end product, insulin is secreted to help the cells utilise glucose.
If more Glucose is available then required for the human body then Insulin stimulates Liver & Muscle cells to Store Glucose as Glycogen.
Glycogen Reserves
Glycogen reserve is about 600g in the human body. This reserve is used in between meals and when you require immediate energy , as in sprinting or running .
It’s also important to remember that 1 g Glycogen is stored with 3 g of water. When glycogen stores are depleted then water is also removed in urine and that explains weight loss when glycogen stores are depleted or weight gained, when glycogen stores are replenished.
How is Glucose converted to FAT in the human body?
If excess glucose is available, then what is required for the body, then the body with help from insulin converts the excess glucose into glycogen to be stored in liver and muscle cells.
We have seen that the glycogen stores would be full around 600g in the human body; After the glycogen stores are full and we keep on increasing the available glucose , then what the body does with this excess glucose is, it’s converted into Fat (Triglycerides) .
How much carbs should be consumed daily?
The Dietary Guidelines for Americans recommends that carbs must make upto 45% to 65 % of your total Daily calories.
What are Your Daily Calorie Requirements as Adults?
Energy requirements vary from one person to another depending on a lot of factors like age, gender and level of physical activity, body compositions and other factors.
| Physical Activity | calories | |
| Men, 60 kgs | Sedentary Work | 2320 |
| Moderate Work | 2730 | |
| Heavy Work | 3490 |
| Physical Activity | Calories | Extra Calories | |
| Sedentary Work | 1900 | ||
| Women , 60 kg | Moderate Work | 2230 | |
| Heavy Work | 2850 | ||
| Pregnancy | + 350 | ||
| Lactation | + 550 |
According to guidelines , 45% to 65% of your calories must come from Carbs. Suppose we assume your daily required carbs is 1900 calories, then;
855 to 1235 calories must be coming from carbs ; which equates to
214 g to 309 g of Carbohydrates as 1 g of Carbohydrates gives 4 Calories.
How much carbohydrates we must consume everyday is important as the body has to maintain the normal blood glucose levels.
What Carbohydrates Should We Eat, Everyday? What are Good Carbs and Bad Carbs?
What you should be eating are Complex Carbohydrates which contains high fibre and are long chain, unprocessed, which take time to digest;
Non- Starchy Vegetables
- Broccoli
- Lettuce
- Cucumber
- Tomatoes
- Green Beans
- radish
- Okra
- Cauliflower
- Mushrooms
Starchy Carbs
- Fruits like Apple, Blueberries, strawberry
- Brown Rice
- Whole Wheat Bread
- Whole Grain Pasta
- Oatmeal
Starchy Vegetables
- Corn
- Green Peas
- Sweet Potato
- Pumpkin
- Plantains
- Black Beans
- Kidney Beans
- Chickpeas
- Green Lentils
What you should be AVOIDING are bad carbs which are listed below, as these raise your blood sugar fast and are bad for your health in the long term,
- Sugary Drinks, Like Cola
- Fruit juices with add sugars
- Bakery items, Like white bread, cookies , pastries and cakes
- Ice cream
- Candies and chocolates
- French fries and potato chips
common Total carbohydrate content of the food stuffs we eat
How many carbohydrates in Banana?
Bananas are a source of high carbs and the type of banana we eat, either raw or ripe, the content of carbohydrate changes .
Ripe Banana has more sugar . Ripe means it’s developed to the point of eating .
Unripe Banana has starch , which means it is yet to become sugar.
- 100 g of Banana has 23 g of carbs
- 81 g ( extra small Banana) has 19 g of carbs
- 118 g ( 1 medium ) has 27 g of carbs
- 136 g ( 1 large size) has 31 g of carbs
- 1 cup sliced 150 g has 34 g of carbs
How many carbohydrates in Oats ?
- 100 g of Oatmeal contains 12g of carbs
- 1 cup ( 234 g ) has 27g of carbs
How many carbohydrates in Potato?
- 100g of potato contains 17 g of carbs
- 1 small potato(170g) contains 30g of carbs
- 1 medium potato (213g) contains of 37 carbs
- 1 large potato (369g) contains 64 g of carbs
How much carbohydrates in Rice?
- 100g of rice contains 28g of carbs
- 1 cup of rice contains 45g of carbs
How many carbohydrates in Apple?
- 100g of apple contains 14g of carbs
- 1 medium apple contains 25g of carbs
How many Carbohydrates in Milk ?
- Milk 1% fat 100g contains 5g of carbs
- 1 cup (244g) contains 12g of carbs
- 100g of powdered milk contains 38g of carbs
How many Carbohydrates in Egg?
- 100g egg boiled contains 1.1g of carbs
- 1 egg omelette contains 0.6g of carbs
- 100g egg poached contains 0.7g of carbs
- 100g egg scrambled contains 1.6g of carbs
![]()