Male Reproductive System
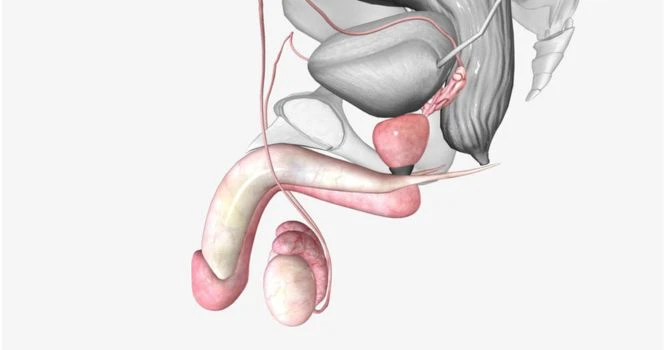
External Genetalia – Male
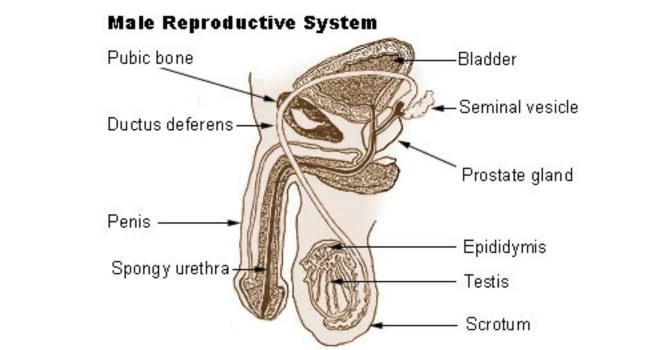
It includes
- Penis
- Scrotum ( is homologous to Labia Majora in females)
Penis : The male genital organ formed by erectile tissues,
1. Corpora Cavernosa – which are two in number
2. Corpus Spongiosum – which surrounds the urethra and terminates as glans penis.
Penile urethra contains mucus glans called, glands of little throughout its length.
Scrotum: The 2 Testes are suspended in a sac like structure called Scrotum.
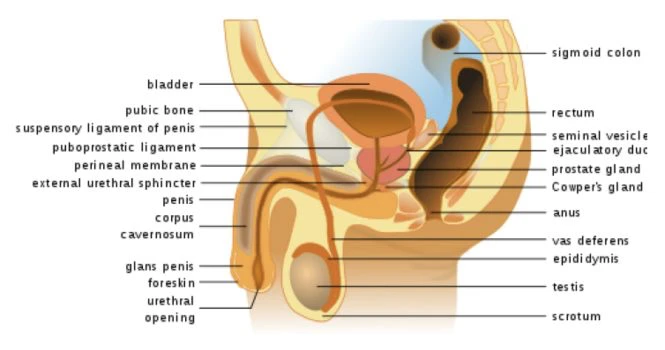
Internal Genital organs
It includes
- Testis
- Epididymis
- Vas deferens
- Seminal vesicle
- Prostate gland
- Penile urethra (is homologous to Labia Minora in females)
Testis: They are the Primary sex organs in Males and are 2 in number. Each weighs around 15g to 19g and are about 5 x 3 cm.
Epididymis: It’s a 4 meter long convoluted tubule.
Vas deferens: Also called ductus deferens or spermatic deferens or sperm duct. At caudal pole or tail end , epididymis turns sharply and continues as vas deferens without any identifiable demarcation.
Seminal vesicle: Secretes seminal fluid which is either neutral or slightly alkaline in nature and forms 60% of the total semen
Prostate gland: Secretes prostatic fluid which is thin, milky and alkaline fluid forming 30% of total semen.
Penile urethra: It’s longest part of male urethra and about 15 cm long.