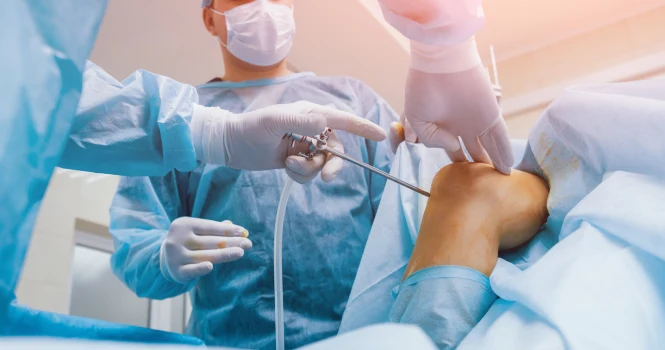
If your knee is damaged severely due to injuries or arthritis, you might find it extremely difficult to walk or climb up the stairs. Sometimes, you might even find it painful even when you aren’t moving. And if nonsurgical treatments, including medicines and walking supports fail to help you, it is recommended that you opt for total knee replacement surgery. Such surgeries are extremely safe and effective in relieving pain and correcting deformities in your legs while helping you with day-to-day activities as well.
What is Total Knee Replacement, and how is it done?
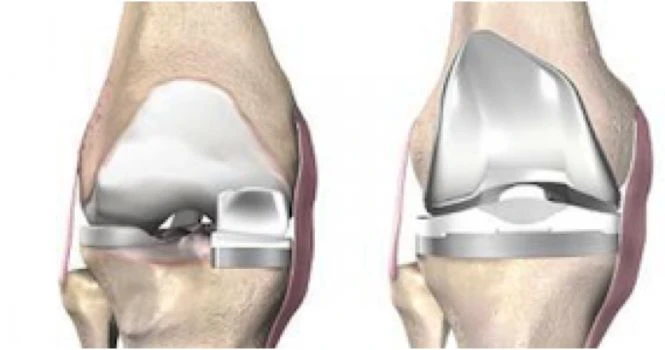
Knee replacement or the Knee Arthroplasty is a surgical procedure that resurfaces your knee, which is damaged due to arthritis or an injury. Plastic or metal parts are used to cap the ends of bones which form the knee joint and the kneecap.
The process of knee replacement surgery involves the following steps:
- Preparing the bone by removing the damaged cartilage surfaces at the ends of tibia and femur along with a small amount of underlying bone.
- Positioning the metal implants : This step involves replacing the removed cartilage with metal components to create the surface of the knee joint. The metal parts may be fitted or cemented into the bone.
- Resurfacing the Knee cap : The knee cap’s undersurface is cut and resurfaced using a plastic button.
- Inserting a plastic spacer between the metal components to create a smooth gliding surface.
What are the conditions that affect the Knee joint?
- Osteoarthritis : An age-related type of arthritis caused due to wear and tear of the knee joints. This condition is quite common among people aged 50 and older but does occur among youngsters as well. This condition affects the knee cartilage to soften and get worn out while causing the bones to rub against each other while causing pain.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a condition in which the synovial membrane which surrounds the joint gets inflamed and thickened. This chronic inflammation damages the cartilage and causes stiffness and pain.
- Post-traumatic arthritis occurs after a serious knee injury. Fractures of the bones that surround the knee or the knee ligaments getting torn might end up damaging the articular cartilage causing knee pain and limited knee function.
Who might be benefitted from a total knee replacement surgery?
- Individuals with severe knee pain or stiffness that limits their mobility
- Moderate to severe knee pain even while at rest
- People who suffer from chronic knee inflammation and swelling that cannot be treated using any medication
- Individuals with knee deformities
There are no age or weight restrictions for this surgery. Recommendations are based on a person’s pain and disability.
What to expect from a total knee replacement surgery?
It has a high success rate with more than 90% of patients who underwent this surgery experiencing a dramatic reduction in knee pain and tremendous improvement in their ability to perform daily activities like walking and climbing the stairs. It is reported that, with appropriate activity modification, knee replacement tends to last for several years.
What are the possible complications of total knee replacement surgery?
Although the complication rate following this surgery is very low, in about less than 2% of the cases, serious complications like knee joint infection can occur. Other medical complications include stroke and heart attack. Here’s a list of a few complications:
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Continued pain
- Neurovascular injury
- Implant problems
How long does this procedure take?
It takes approximately 1-2 hours to complete total knee replacement surgery. However, you might need to stay in the hospital for a few days.
How to ensure success of the surgery?
- Pain management : As a natural part of the healing process, you might feel some pain, for which you will be prescribed drugs such as opioids, NSAIDs, and local anesthetics.
- Blood Clot Prevention : You will be prescribed blood thinners or compression boots to prevent blood clotting.
- Physical therapy : Your physical therapist will teach you specific exercises to strengthen your leg and knee movements soon after the surgery.
- Wound Care : After removing the stitches or staples, you need to avoid soaking the wound in water and wait until it has thoroughly dried.
- Diet : Although you might experience loss of appetite for several weeks, it is recommended that you follow a balanced diet along with iron supplements to help in wound healing and restoring muscle strength.
How to protect the new Knee replacement?
- Perform light physical activities regularly
- Take precautions to prevent injuries and falls
- Regular checkups with your orthopedic surgeon for routine follow-up exams
More than 90% of today’s knee replacement surgeries are functioning well even after 15 years post the surgery. When you follow your surgeon’s instructions and take proper care, the success of the surgery can be ensured.