Hair transplant or Hair Transplantation Surgery is a fascinating topic that blends medicine, aesthetics, and personal well-being, and it’s more relevant now than ever before. We will look into Hair Transplant in India in greater depth in this article.
Primarily used to treat male pattern baldness, hair transplants have also found use in restoring eyelashes, eyebrows, beard hair, chest hair, and filling in scars caused by accidents or surgery.
We’ll delve into the science that underpins these procedures, explore various hair transplant techniques, guide you through the process of getting a hair transplant in India, and discuss potential risks and complications.
So, whether you’re considering a hair transplant or simply curious about the process, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need. Let’s get started!
What is Hair Transplant?
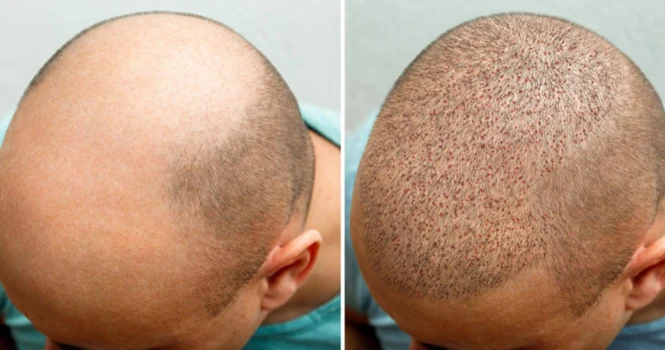
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that helps treat baldness. The process involves taking hair follicles from a part of the body known as the ‘donor site,’ typically the back or sides of the scalp where hair growth is still plentiful, and transferring them to the ‘recipient site,’ which is the area suffering from hair loss or thinning.
This procedure is most commonly used to treat male pattern baldness, a genetic condition that affects many men as they age.
However, hair transplants can also be used to restore hair in other areas, such as the eyelashes, eyebrows, or beard, and to cover scars from accidents or previous surgeries.
The goal of a hair transplant is to restore growth to areas of the scalp that have experienced hair loss.
The new hair growth from the transplanted follicles will generally continue to grow like the rest of the patient’s hair.
Types of Hair Transplant
There are two main types of hair transplant procedures:
- Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and
- Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
Each has its pros and cons, and the choice between the two often depends on the individual patient’s needs, the extent of their hair loss, and their personal preferences.
Remember that while hair transplants can produce significant improvements, they cannot create a completely full head of hair if the hair loss is extensive.
It’s always recommended to have a consultation with a qualified professional to understand the expected outcomes and to discuss the best approach for your specific circumstances.
Causes of Hair Loss
Hair loss, also known as alopecia, can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
1. Genetics: The most common cause of hair loss is hereditary male- or female-pattern baldness. This typically happens with aging and in predictable patterns—a receding hairline and bald spots in men and thinning hair in women.
2. Hormonal Changes and Medical Conditions: A variety of conditions can cause temporary or permanent hair loss, including hormonal changes due to pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, and thyroid problems. Medical conditions include alopecia areata, which involves the immune system targeting hair follicles, and scalp infections like ringworm.
3. Medications and Supplements: Hair loss can be a side effect of certain drugs, such as those used for cancer, arthritis, depression, heart problems, gout, and high blood pressure.
4. Radiation Therapy to the Head: The hair may not grow back the same as it was before.
5. Highly Stressful Events: Many people experience a general thinning of hair several months after a physical or emotional shock. This type of hair loss is temporary.
6. Hairstyles and Treatments: Excessive hairstyling or hairstyles that pull your hair tight, such as pigtails or cornrows, can cause a type of hair loss called traction alopecia. Hot-oil hair treatments and permanents can cause inflammation of hair follicles that leads to hair loss. If scarring occurs, hair loss could be permanent. (Permanents, or perms, involve chemically altering the hair to change its natural texture, often to add curls or waves.)
7. Poor Nutrition: Deficiencies in nutrients such as iron, vitamin A, vitamin B complex, and protein can lead to hair loss.
8. Underlying Disease: Conditions like lupus or diabetes can result in hair loss.
Remember, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider if you’re experiencing hair loss. They can provide you with a diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
The Impact of Hair Loss on Quality of Life
Hair loss can have significant psychological and social impacts on an individual’s life, affecting their quality of life in various ways:
1. Self-esteem and Body Image: Hair is often associated with beauty and youth. As such, hair loss can lead to decreased self-esteem and a negative body image. Individuals may feel less attractive and experience dissatisfaction with their appearance, which can impact their confidence in social or professional settings.
2. Social Functioning: Hair loss can influence an individual’s social interactions and relationships. For example, it can cause fear of rejection or ridicule, leading to social withdrawal or avoidance of certain social situations.
3. Emotional Well-being: Hair loss can lead to psychological distress, including feelings of embarrassment, depression, and anxiety. It can also cause a preoccupation with hair loss, with individuals constantly worrying about their changing appearance.
4. Stress and Mental Health: Dealing with hair loss can lead to increased stress, which can, in turn, exacerbate hair loss. In severe cases, individuals may experience conditions such as body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) or trichotillomania (hair-pulling disorder).
6. Financial Impact: The cost of hair loss treatments, from over-the-counter products to surgical procedures like hair transplants, can be substantial, adding a financial burden.
It’s important to note that everyone responds differently to hair loss, and the impact on quality of life can vary greatly from person to person.
However, understanding these potential impacts can help in developing coping strategies and seeking appropriate treatment and support. It’s also crucial to remember that professional help, including mental health services, is available for those struggling with the emotional aspects of hair loss.
The Science behind Hair Transplants
A. Explanation of the Biological Principles behind Hair Transplants
1. Understanding Hair Growth Cycle: Human hair grows in cycles. Each hair follicle goes through phases of growth (anagen), regression (catagen), rest (telogen), and then shedding (exogen). This cycle repeats throughout our lives. At any given time, each hair on our head is at a different stage of this cycle.
2. Follicular Units: Hair grows in groupings known as follicular units, each containing one to four hair strands. A follicular unit also includes sebaceous (oil) glands, nerves, a small muscle, and occasionally, a vellus hair (a fine, short hair that’s barely noticeable). In a hair transplant, these follicular units are extracted and transplanted as they are to ensure natural-looking results.
3. Donor Dominance Theory: This concept is the cornerstone of hair transplantation. According to the principle of donor dominance, hair follicles retain their original characteristics regardless of their new location.
So, when hair follicles are moved from a region unaffected by baldness (donor site, usually the back or sides of the head) to a balding area (recipient site), they continue to grow as if they were still in their original location.
This means the transplanted hair is resistant to the hormones that cause baldness and will continue to grow in the new location.
4. Angulation: The angle at which hair grows differs across the scalp. Surgeons aim to mimic these natural growth angles when transplanting the follicular units to make the results look as natural as possible.
5. Hair Type and Color: Hair characteristics like color, thickness, and curliness can affect the perception of density and coverage.
Lighter hair colors, coarser hair, and curly hair give an impression of higher density than darker, finer, or straight hair. This principle is considered when planning a hair transplant.
6. Wound Healing: After the follicular units are transplanted, the healing process begins. The body’s natural wound healing response helps secure the grafts into place and facilitates the growth of new hair from the transplanted follicles.
7. Hair Growth Post Transplant: After a hair transplant, the transplanted hairs typically fall out within a few weeks. This is normal and is a part of the hair growth cycle. New hair growth from the transplanted follicles starts after a few months.
Remember, while the biological principles of hair transplantation are scientifically sound, individual results can vary based on factors such as overall health, age, the extent of hair loss, and adherence to post-operative care.
B. A Look into the Role of Follicular Units
1. What are Follicular Units?
Follicular units are naturally occurring groups of hair follicles on the scalp. A single follicular unit usually contains one to four hair follicles, sebaceous (oil) glands, nerves, a tiny muscle (the arrector pili), and a fine vellus hair.
2. The Importance of Follicular Units in Hair Transplants
Follicular units are a crucial component of modern hair transplant procedures for several reasons:
- Natural Appearance: Hair on the scalp grows naturally in these groupings, not as individual strands. Transplanting entire follicular units helps to mimic this natural pattern and achieve results that look normal and undetectable as transplants.
- Efficiency of Transplantation: Because each follicular unit can contain up to four hairs, using these units can allow for a more efficient transplantation process. A surgeon can transplant more hair using fewer incisions, which can result in a less invasive procedure and potentially faster healing times.
- Maximize Survival Rate: By keeping the follicular units intact during extraction, it preserves the sebaceous glands and tiny blood vessels around the follicles, enhancing the survival rate of the transplanted hairs.
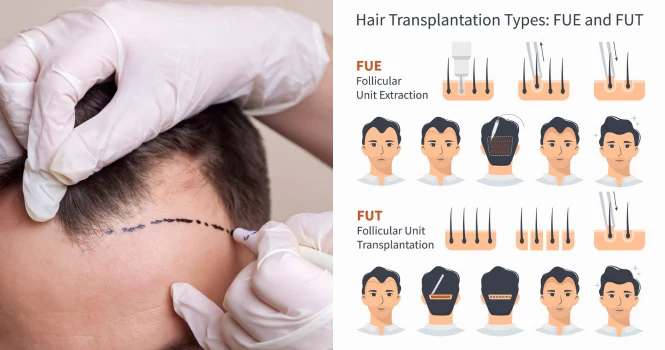
3. Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) & Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT):
These are the two primary techniques for harvesting follicular units during a hair transplant.
FUT involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area, and the follicular units are then dissected from this strip under a microscope.
FUE, on the other hand, involves removing follicular units directly from the scalp one at a time, without a strip of skin being removed.
Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two often depends on the individual’s needs, lifestyle, and the surgeon’s expertise.
4. Placement of Follicular Units:
The placement of follicular units during a hair transplant needs careful consideration. The surgeon has to follow the natural hair direction and distribution to ensure a realistic hair pattern. They also need to consider the density of the units to achieve a satisfactory level of coverage.
C. Understanding How Hair Growth Cycle Affects the Transplant Process
The human hair growth cycle is composed of four distinct stages:
- Anagen (growth phase)
- Catagen (transition phase)
- Telogen (resting phase)
- Exogen (shedding phase).
Each hair on our scalp is at a different stage of this cycle at any given time, which is why we don’t lose all our hair at once.
The understanding of this cycle is crucial to the hair transplant process and its effectiveness. Here’s why:
1. Harvesting in Anagen Phase: Ideally, the hairs for transplantation are harvested from the donor area when they are in the anagen phase.
During this stage, the hair follicles are active and producing new hair cells, leading to hair growth.
These actively growing hairs are considered healthier and more robust, resulting in a higher chance of survival when transplanted.
2. Shedding Post Transplantation (Telogen Effluvium): After hair transplantation, it is common for the transplanted hairs to enter into the telogen phase and shed. This process, known as “shock loss” or “telogen effluvium,” typically occurs a few weeks after the procedure.
This is a normal part of the process and does not mean the procedure was unsuccessful. The transplanted hair follicles are still intact and will re-enter the anagen phase after some time.
3. Hair Regrowth Post Transplantation: Around 2 to 4 months post-procedure, the transplanted hair follicles re-enter the anagen phase, resulting in new hair growth.
It’s important to note that this growth will be gradual, and full results are typically seen after 12 to 18 months. This process can sometimes be slower or faster, depending on individual factors like overall health, age, and hair quality.
4. Longevity of Transplanted Hair: Transplanted hair follicles retain their characteristics from the donor site. Therefore, they are genetically programmed to resist the hormones that cause hair loss.
Once the transplanted hair has grown, it will continue to do so for a lifetime, provided that no other medical or scalp conditions affect its growth.
Hair Transplant Techniques
A. Detailing the Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
1. What is Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)?:
FUT, also known as the strip method, is a hair transplant technique where a strip of skin with hair is removed from the back or sides of the head (the donor site). This strip is then divided into individual follicular units, each containing 1-4 hairs, which are then transplanted into the bald or thinning areas of the scalp.
2. Procedure:
The FUT process can be broken down into a few steps:
- Preparation: The surgeon will begin by trimming a strip area on the back or sides of the scalp. The patient’s remaining hair will cover the area after the procedure.
- Removal of the Strip: The surgeon will then surgically remove a strip of the scalp under local anesthesia. The size of the strip depends on the number of grafts needed.
- Closing the Wound: The surgeon will then close the wound, typically leaving a linear scar that is hidden by the surrounding hair.
- Preparation of the Grafts: Skilled technicians will use specialized microscopes to dissect the strip into individual follicular units without damaging the hair follicles.
- Transplantation: The surgeon will then create small holes in the recipient areas and place the follicular units into these holes.
The placement is done carefully to mimic the natural hair growth pattern, ensuring a natural-looking result.
3. Advantages of FUT:
- Larger Areas: FUT allows for the transplantation of a large number of grafts in a single session. It’s therefore often preferred for patients with significant hair loss.
- Graft Quality: As the grafts are extracted in a strip and dissected under direct visualization, the follicles are less likely to be damaged, resulting in a high-quality graft.
- Cost-Effective: FUT is typically more cost-effective than other methods, as it allows for a large number of grafts to be transplanted in a single session.
4. Disadvantages of FUT:
- Scarring: FUT leaves a linear scar on the back of the head. While this scar is typically concealed by the surrounding hair, it may be visible if the patient has very short hair.
- Recovery Time: As FUT is a more invasive procedure, the recovery time can be slightly longer than with other methods.
- Donor Area Pain: Some patients may experience discomfort in the donor area post-surgery due to the removal of the strip.
5. Who is FUT Suitable For?:
FUT is typically recommended for individuals who have large areas of baldness, are not bothered by the possibility of a linear scar, or who plan to keep their hair long enough to cover the scar. It’s also suitable for those seeking a more affordable hair transplant method.
B. Explaining the Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
1. What is Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)?:
FUE is a hair transplant method that involves extracting individual follicular units directly from the scalp’s donor area (typically the back and sides of the head) and transplanting them to the balding or thinning areas.
Unlike FUT, FUE does not require the removal of a strip of scalp.
2. Procedure:
The FUE process can be broken down into a few steps:
- Preparation: The surgeon will shave the patient’s donor area, revealing the individual hair follicles.
- Extraction of the Follicular Units: Using a small punch tool, the surgeon will make a tiny circular incision around a follicular unit to isolate a graft. The graft is then extracted directly from the scalp using a tweezer-like tool. This process is repeated until the surgeon has enough grafts for the procedure.
- Preparation of the Recipient Area: The surgeon will prepare the balding or thinning areas for transplantation, creating small holes or slits.
- Transplantation: The extracted follicular units are then placed into the prepared areas. The placement is done carefully to ensure the transplanted hair will grow in the natural direction and to create a dense, natural-looking hairline.
3. Advantages of FUE:
- No Linear Scar: As FUE extracts individual follicular units instead of a strip of scalp, it doesn’t leave a noticeable linear scar. This makes FUE an attractive option for those who wish to wear their hair very short.
- Less Post-Operative Discomfort: As FUE is less invasive than FUT, patients generally experience less discomfort after the procedure and the healing process is quicker.
- Versatility: FUE can be used to transplant hair to other body areas, such as eyebrows or beard.
4. Disadvantages of FUE:
- Time-Consuming: As each follicular unit is removed individually, FUE procedures can be more time-consuming than FUT procedures.
- Higher Cost: Due to the length and complexity of the procedure, FUE is typically more expensive than FUT.
- Lower Graft Yield: As the extraction is done individually, there may be a lower yield of grafts compared to FUT, especially in patients with limited donor areas.
5. Who is FUE Suitable For?:
FUE is often recommended for individuals who have a limited donor supply, those who have a tight scalp or previous scars, and individuals who prefer to wear their hair very short.
It’s also suitable for those who are willing to pay more for a less invasive procedure with minimal scarring.
C. Comparing and contrasting FUT and FUE
| Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) | Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) | |
| Definition | A method where a strip of scalp is removed from the donor area, and the hair follicles are then separated and implanted. | A method where individual hair follicles are directly extracted from the donor area and implanted. |
| Procedure | More invasive as it involves the surgical removal of a strip of scalp. | Less invasive as it involves the extraction of individual follicular units. |
| Scarring | Leaves a linear scar in the donor area, which can be covered with hair. | Leaves tiny dot scars in the donor area, less noticeable especially with short hair. |
| Number of Grafts | Allows for a larger number of grafts to be transplanted in a single session. | May not facilitate as many grafts per session, depending on the donor area’s density. |
| Surgery Time | Typically less time-consuming as many grafts are obtained from a single strip. | More time-consuming as each follicular unit needs to be individually extracted. |
| Recovery | Slightly longer recovery due to the surgical wound in the donor area. | Quicker recovery as it is less invasive. |
| Cost | Generally more cost-effective as more grafts can be transplanted in a single session. | Generally more expensive due to the time and expertise required for individual extraction. |
| Ideal For | People with larger areas of baldness, those who aren’t bothered by a potential scar, or those preferring a more affordable method. | People with limited donor supply, those with tight scalps or previous scars, individuals who prefer to wear their hair very short, and those who prefer a less invasive procedure. |
D. Discussion on Newer, Less common techniques
1. Robotic Hair Transplants:
Robotic hair transplantation is a relatively new procedure that uses advanced robotic technology to aid the surgeon in the hair transplant process. The ARTAS system is one of the most well-known robotic systems in this field.
- Procedure: It uses advanced algorithms to identify and select the best follicular units for extraction, making precise incisions around each follicular unit. The extracted grafts are then manually implanted into the recipient area.
- Advantages: It provides significant improvements in precision, accuracy, and speed over traditional manual methods, minimizing the risk of human error. It also minimizes damage to the grafts, resulting in a higher survival rate.
- Limitations: As with any advanced technology, it is not free from limitations. The initial cost of equipment and the cost to the patient can be quite high. Furthermore, while the extraction process is automated, the implantation of grafts is still performed manually.
2. Stem Cell Hair Transplants:
This technique, which is still under research and not widely available, involves multiplying hair cells in a lab from a small sample of the person’s scalp tissue and then injecting these cells into bald areas of the scalp.
- Procedure: The aim is to stimulate new hair follicles to grow, making it potentially a more effective solution for people with widespread hair loss.
- Advantages: The main advantage is the potential to produce a much larger amount of hair compared to traditional transplants.
- Limitations: However, the procedure is still in the experimental stages, and its effectiveness and safety are not yet fully established.
3. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
While not a hair transplant technique per se, PRP therapy is increasingly used in conjunction with hair transplants to promote hair growth.
- Procedure: It involves drawing a small amount of the patient’s blood, processing it to isolate the platelet-rich plasma, which is then injected into the patient’s scalp.
- Advantages: PRP contains growth factors that can stimulate hair growth, enhance the survival of the transplanted grafts, and accelerate the healing process.
- Limitations: PRP therapy requires multiple sessions and its effectiveness can vary from person to person.
It’s important to remember that while these new techniques are promising, they may not be suitable for everyone.
Always consult with a knowledgeable and experienced hair transplant specialist to discuss your options and decide on the best approach for your specific situation.
The Process of Getting a Hair Transplant
A. How to Determine If You’re a Good Candidate for Hair Transplant
A hair transplant can provide significant improvements for individuals experiencing hair loss, but it’s not suitable for everyone. Here are several factors to consider:
1. Extent and Pattern of Hair Loss: Hair transplants are most successful for those with male or female pattern baldness, a genetic condition that causes hair to recede and thin in predictable patterns.
It’s less effective for individuals who have unpredictable or diffuse hair loss, such as alopecia areata.
2. Hair Type: Certain hair characteristics, such as thickness, color, and curliness, can affect the results of a hair transplant. For example, individuals with thicker or curly hair might achieve better coverage with fewer grafts compared to those with thin or straight hair.
3. Age: Age is a significant factor to consider. While there’s no strict age limit for a hair transplant, many surgeons advise against the procedure for younger patients, typically those in their 20s, who may not yet have a defined pattern of hair loss.
As hair loss is progressive, younger patients might find that their hair continues to thin and recede after the transplant, leading to unnatural-looking results.
4. General Health: As with any surgical procedure, candidates for a hair transplant should be in good general health.
Certain health conditions, such as heart disease, autoimmune disorders, or uncontrolled diabetes, might increase the risks associated with surgery or affect the healing process.
5. Donor Hair Availability: A successful hair transplant relies on having a sufficient amount of healthy donor hair. Individuals with a good amount of thick and healthy hair at the back and sides of the scalp are usually the best candidates.
Conversely, those with limited donor hair might not achieve their desired results.
6. Expectations: It’s essential for candidates to have realistic expectations about what a hair transplant can achieve.
While the procedure can significantly improve your appearance and boost your self-confidence, it might not restore your hair to its original thickness or create a completely full head of hair.
Finally, a consultation with a skilled hair transplant surgeon is the best way to determine whether you’re a good candidate.
They can assess your hair loss, discuss your goals and concerns, and recommend the best treatment options for your specific needs.
B. What to Expect in the Initial Consultation
The initial consultation for a hair transplant is a crucial step in your hair restoration journey. It provides an opportunity for you to discuss your concerns, expectations, and to receive a comprehensive assessment of your hair loss. Here’s what you can expect:
1. Medical History Assessment: The surgeon will start by asking about your medical history, including any underlying health conditions, medications you’re currently taking, previous surgeries, and any allergies.
They’ll also want to know about your family’s history of hair loss, as this could influence your treatment plan.
2. Physical Examination: The surgeon will perform a thorough examination of your hair and scalp.
This usually involves using a device called a densitometer to measure the density of hair in the donor areas, assessing the pattern and stage of your hair loss, and possibly taking photographs for reference.
3. Discussion of Goals and Expectations: The surgeon will discuss your goals for the procedure and what you hope to achieve. It’s important to be open and honest during this discussion.
The surgeon will also talk about what’s realistically achievable, given your degree of hair loss, the density of your donor hair, and other factors.
4. Treatment Options: Based on the assessment, the surgeon will recommend the most suitable hair transplant method for you, such as FUT or FUE.
They’ll explain the procedure, including the steps involved, the expected results, and the risks and potential complications.
5. Cost Estimation: Hair transplant costs can vary based on many factors, including the number of grafts required, the technique used, the surgeon’s experience, and the location of the clinic.
The surgeon or a clinic representative should provide a cost estimate for the procedure.
6. Opportunity for Questions: The consultation is your opportunity to ask any questions you might have.
You might want to ask about the surgeon’s experience, the number of procedures they’ve performed, the expected recovery time, and any potential risks or complications.
The initial consultation should leave you with a clear understanding of your options and what to expect from a hair transplant.
You should never feel pressured to make a decision right away. Take your time to consider the information, do further research if needed, and feel free to seek a second opinion.
C. Breakdown of the Procedure: From Preparation to Post-Operative Care
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that requires careful preparation, a meticulous surgical process, and dedicated post-operative care to ensure the best results.
Here’s a breakdown of the steps involved:
A. Preparation for Surgery
1. Pre-Operative Assessment: Before the surgery, your surgeon will perform a pre-operative assessment to confirm your health status. This may include blood tests or other diagnostic procedures.
2. Instructions: Your surgeon will give you a set of instructions to follow before the procedure. This can include avoiding certain medications and alcohol, ensuring you have a healthy diet, and arranging for transportation on the day of surgery since you may not be able to drive afterward.
B. Day of Surgery
- Arrival at the Clinic: You’ll arrive at the clinic where the staff will check you in, confirm your details, and prepare you for the procedure.
- Anesthesia: The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, meaning you’ll be awake but won’t feel any pain in the treated area.
- Donor Area Preparation: Depending on the method used (FUT or FUE), the donor area at the back or sides of your scalp will be prepared. This could involve shaving and marking the area.
- Extraction of Hair Follicles: The surgeon will then extract hair follicles from the donor area. In FUT, this involves removing a strip of scalp, while in FUE, individual follicular units are extracted.
- Preparation of the Recipient Area: The surgeon will create small incisions or holes in the recipient area where the grafts will be placed.
- Implantation of Hair Follicles: The extracted hair follicles are then implanted into the prepared recipient area.
C. Post-Operative Care
- Immediately After the Procedure: After the procedure, your scalp will be bandaged and you’ll be given post-operative care instructions. These typically include how to care for your scalp, which medications to take, and when to return for a follow-up appointment.
- Home Care: At home, you’ll need to be gentle with your scalp and avoid activities that could dislodge the grafts, like vigorous washing or scratching.
- Follow-up Appointments: You’ll have follow-up appointments with your surgeon to check your progress and to remove any non-absorbable sutures (if you had an FUT procedure). This usually happens around 10 days after the procedure.
- Growth of Transplanted Hair: You can expect to see new hair growth starting three to four months after the procedure. However, it often takes six to twelve months to see the full results.
Remember, the most important part of this journey is to follow your surgeon’s instructions closely at every stage of the process. This will help to ensure that your transplant is successful and that your new hair will last for many years to come.
Risks and Complications
A. Detailed Discussion on Potential Risks
As with any surgical procedure, hair transplants come with potential risks and complications. It’s important to have a thorough understanding of these before deciding to proceed. Here are the most common risks associated with hair transplant surgery:
A. Infection and Bleeding: Although rare, there’s a small risk of infection and bleeding during and after the surgery. Proper post-operative care can significantly minimize these risks.
B. Scarring: Scarring is more common with the FUT method due to the removal of a strip of skin from the back of the scalp. These scars are usually hidden under the hair and fade over time, but they may be visible if you have short hair. FUE leaves small dot-like scars that are less visible.
C. Unnatural-Looking Results: If the procedure isn’t performed by an experienced surgeon, it could result in an unnatural appearance, such as a patchy hair pattern or a hairline that doesn’t look natural.
D. Damage to Existing Hair Follicles: There’s a risk that the surgery could damage existing hair follicles near the transplant site, leading to additional hair loss. This is more likely if the procedure is performed by an inexperienced surgeon or if the recipient site isn’t properly prepared.
E. Failure of Hair Grafts: Not all hair grafts will successfully take root in the transplant site. Some may not survive the transplant process, leading to less density than initially expected. This is more likely if the grafts aren’t properly handled and implanted.
F. Swelling and Pain: Some degree of swelling and discomfort is common after the procedure, usually around the forehead and eyes. This typically subsides within a few days. Pain can be managed with prescribed medications.
G. Folliculitis: This is an infection or inflammation of the hair follicles that can cause redness, swelling, and sometimes small, pus-filled blisters. It’s typically treated with antibiotics and compresses.
H. Post-Operative Shock Loss: Some patients may experience temporary hair loss in the weeks following the procedure. This is known as shock loss and it’s usually temporary.
I. Psychological Impact: The initial shedding phase and the wait for new growth can be emotionally challenging for some patients. It’s important to have realistic expectations and to understand that the full results won’t be visible until several months after the procedure.
While these risks can sound alarming, they are relatively rare, especially when the procedure is performed by an experienced and qualified surgeon.
During your consultation, it’s important to discuss these risks with your surgeon and to understand how they apply to your specific situation.
B. How to Handle Complications
Even with the most skilled surgeon and meticulous care, complications can arise from hair transplant surgery. Here’s how to handle these potential issues:
1. Recognize the Signs: Early recognition of complications is key. If you notice excessive pain, swelling, redness, pus, or bleeding at the transplant or donor site, contact your surgeon immediately. Additionally, fever, dizziness, or unexpected hair loss should be reported.
2. Contact Your Surgeon: If you suspect you’re experiencing a complication, your first point of contact should be your surgeon or the clinic where the procedure was performed. They can provide guidance and may want to see you for a follow-up appointment to assess the issue.
3. Follow Medical Advice: If a complication is identified, it’s crucial to follow your surgeon’s advice. This may include taking prescribed medications, applying topical treatments, or in rare cases, additional surgery.
4. Patience: Some complications, like shock loss or slow hair growth, can be disheartening but often resolve with time. Remember, the full results of a hair transplant can take up to a year to show.
5. Second Opinions: If you’re not satisfied with the advice or treatment from your surgeon, don’t hesitate to seek a second opinion. It’s your right as a patient to feel confident and comfortable in your healthcare decisions.
Remember, complications are rare and can often be prevented through careful surgeon selection, adherence to pre- and post-operative care instructions, and maintaining good overall health.
Always approach a hair transplant procedure with a thorough understanding of the risks and potential complications, and don’t hesitate to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
C. Measures to Mitigate Risks
While risks are inherent in any surgical procedure, including hair transplants, several measures can be taken to reduce these potential complications. Here’s how you can proactively mitigate risks:
1. Choose a Reputable Surgeon: Selecting a qualified, experienced hair transplant surgeon is perhaps the most critical step in minimizing risk.
Ensure the surgeon is certified by a recognized medical board and has extensive experience with hair transplant procedures.
Don’t hesitate to ask about their complication rates and to see before-and-after photos of previous patients.
2. Follow Pre-Operative Instructions: Your surgeon will provide specific instructions to prepare for the procedure, including medications to avoid, dietary guidelines, and hygiene practices.
Following these directives can reduce the risk of bleeding, infection, and other complications.
3. Maintain Good Overall Health: Being in good health can help reduce the risk of complications. This includes eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and avoiding habits like smoking or excessive drinking, which can hinder healing and increase the risk of complications.
4. Follow Post-Operative Care Guidelines: Adhering to the post-operative care instructions given by your surgeon is crucial. This will include directives on how to clean and care for the surgical sites, medications to take to aid healing and reduce the risk of infection, and when to resume normal activities.
5. Keep Follow-Up Appointments: These appointments allow your surgeon to monitor your healing process and spot any signs of complications early. Even if you feel fine, don’t skip these appointments.
6. Communication: Keep open lines of communication with your healthcare provider. If you’re unsure about a symptom or have concerns, it’s better to voice them early rather than wait for complications to develop.
By taking these proactive steps, you can help ensure a smoother procedure and recovery process, minimizing the likelihood of complications from your hair transplant.
The Effectiveness and Longevity of Hair Transplant
A. Expected Results and Success Rates
Hair transplants have been proven to be an effective solution for hair loss, with many patients experiencing significant improvements in hair coverage and density. However, it’s important to note that results can vary based on a number of factors.
1. Expected Results: The goal of a hair transplant is to restore hair to areas of the scalp that have become thin or bald. Post-procedure, it can take anywhere from 6 to 12 months, sometimes longer, for the transplanted hair to fully grow in and for the final results to be apparent. The outcome depends on the quality of the donor hair, the area’s size that needs coverage, and the desired density.
2. Success Rates: The success rate of hair transplant surgery largely depends on the skill and experience of the surgeon and the overall health of the patient.
However, generally speaking, about 80-90% of the transplanted hair grafts usually successfully grow in the transplanted area, as long as the grafts are properly cared for and the post-operative instructions are closely followed.
C. Factors Influencing Results: Several factors can affect the results of a hair transplant, including the quality and density of the donor hair, the patient’s age, the extent of hair loss, and the patient’s overall health, including whether or not they smoke (as smoking can impair wound healing and hair growth).
It’s important to remember that while a hair transplant can significantly improve the appearance of thinning or balding hair, it doesn’t prevent further hair loss in other areas of the scalp.
Therefore, some patients may require additional procedures down the line, especially if they continue to lose hair in other areas. As always, setting realistic expectations and consulting with an experienced professional is key to a successful outcome.
B. How to Maintain the Results
Once you’ve undergone a hair transplant, it’s important to take steps to maintain the results and ensure the health of your new hair. Here are some recommendations:
1. Follow Post-Operative Instructions: Carefully follow all post-operative care instructions provided by your surgeon. This can include guidelines on washing your hair, using certain hair products, and taking prescribed medications.
2. Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle: The health of your hair is closely tied to your overall health. Maintain a balanced diet, rich in vitamins and minerals that support hair health, such as vitamin E, vitamin B, iron, and zinc.
Regular exercise can also support healthy circulation, which is beneficial for hair growth.
3. Avoid Damaging Hair Practices: Avoid hair practices that can damage hair and hair follicles. This includes the use of harsh chemicals, like dyes or relaxers, and avoiding hairstyles that pull on the hair, like tight braids or ponytails.
4. Quit Smoking: Smoking can impair circulation and negatively affect the health of your hair. If you’re a smoker, quitting will not only improve your overall health but also help maintain your hair transplant results.
5. Sun Protection: Protect your scalp from excessive sun exposure, especially in the months following your surgery as this can damage the new grafts. Wear a hat or apply a sunscreen specifically designed for the scalp.
6. Regular Check-ups: Regularly schedule follow-up appointments with your surgeon to ensure that your hair is growing as expected and that there are no complications from the surgery.
Remember, a hair transplant does not prevent future hair loss in non-transplanted areas of the scalp.
Therefore, a preventative approach that includes medical treatments, like minoxidil (Rogaine) or finasteride (Propecia), might be recommended by your doctor. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting or stopping any medications or supplements.
C. The Reality of Needing Multiple Procedures
A hair transplant can significantly improve the appearance of thinning or balding hair, but it’s important to have realistic expectations.
One aspect to consider is the potential need for multiple procedures. Here’s why:
1. Progressive Nature of Hair Loss: Hair loss is usually a progressive condition. While a hair transplant can restore hair to thin or bald areas, it doesn’t stop hair loss in other areas of the scalp. Over time, you may experience additional hair loss that requires further treatment.
2. Achieving Desired Density: Depending on the extent of hair loss and your desired outcome, one procedure may not provide the hair density you’re hoping for. Achieving a natural-looking, full head of hair often requires multiple sessions, especially in cases of significant hair loss.
3. Individual Growth Rates: Each person’s hair growth rate and the success of the transplant can vary. Some patients may find that not all of the transplanted hair follicles grow as expected, requiring additional procedures to fill in these areas.
4. Refining the Hairline: Over time, as the face and scalp continue to age, some patients opt for additional procedures to refine the hairline or increase density in certain areas.
5. Limitation of Donor Area: The number of grafts that can be harvested in a single session is limited by the availability of donor hair. For extensive hair loss, several sessions might be required to fully cover the balding areas.
Having multiple hair transplants is not uncommon, and many patients undergo two or three procedures to achieve their desired results.
However, each patient is unique, and the number of procedures required will depend on individual circumstances.
A consultation with an experienced hair transplant surgeon can provide a more accurate assessment based on your specific situation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does the Procedure Hurt?
Most patients experience minimal discomfort during the procedure, as local anesthesia is used. After the procedure, any discomfort or pain can usually be managed effectively with over-the-counter or prescribed pain medication.
How long does the procedure take?
The length of the procedure can vary depending on the number of grafts being transplanted and the technique used, but most procedures take between 4 to 8 hours.
When will I see results?
After the surgery, transplanted hair will typically fall out after 2-3 weeks. New growth starts to appear after 3-4 months, with full growth and results typically seen after 10-12 months.
Can a hair transplant fail?
Although rare, hair transplants can fail if the transplanted hair follicles don’t “take” to the new location. This can occur due to factors such as poor post-operative care, infection, or certain underlying medical conditions.
Can I use someone else’s hair for the transplant?
No, hair for the transplant has to come from your own scalp. Transplanting someone else’s hair would likely lead to the hair being rejected by your body’s immune system.
Will a hair transplant look unnatural?
Modern hair transplant techniques create a very natural appearance when performed by experienced surgeons. Individual follicular units are placed in a pattern that mimics natural hair growth.
Are hair transplants only for men?
While hair transplants are commonly associated with treating male pattern baldness, the procedure is also effective for women experiencing hair thinning or loss.
Can a hair transplant prevent future hair loss?
While a hair transplant can fill in areas of hair loss, it doesn’t stop the progression of hair loss. Additional treatments, like medication or future transplants, may be needed to address ongoing hair loss.
If you are looking for Hair Transplant Surgeon, then send us your details on info@irastoworldhealth.com. Our Team would be able to guide you in the treatment process in India only.