Most common type of cancer, among all cancers worldwide
According to World Health Organisation,
- Among men, the 5 most common sites of cancer diagnosed in 2012 were lung, Prostate, colorectal, stomach, and liver cancer.
- Among women, the 5 most common sites diagnosed were breast, colorectal, lung, cervix, and stomach cancer.
Around one third of cancer deaths are due to the 5 leading behavioral and dietary risks:
- High body mass index
- Low fruit and vegetable intake
- Lack of physical activity
- Tobacco use
- Alcohol use
Tobacco use is the most important risk factor for cancer causing around 20% of global cancer deaths and around 70% of global lung cancer deaths.
Cancer causing viral infections such as HBV/HCV and HPV are responsible for up to 20% of cancer deaths in low and middle-income countries.
More than 60% of world’s total new annual cases occur in Africa, Asia and Central and South America. These regions account for 70% of the world’s cancer deaths.
Types of Lung Cancer:
There are 3 main types of Lung Cancers
1) Non-small cell lung cancer (85%)
- Squamous cell (epidermoid) carcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma
- Large cell (undifferentiated) carcinoma
2) Small cell lung cancer(10%–15%)
3) Lung carcinoid tumor(5%)
General symptoms of lung cancer are listed below but most of them are seen at a later stage of the disease when the disease has progressed to more advanced stage.
- Having cough most of the time
- A change in a cough pattern you have had for a long time
- Shortness of breath, wheezing or hoarseness
- Sputum with signs of blood in it
- An ache or pain when breathing or coughing
- Loss of appetite
- Tiredness
- Unresolving chest infections
- Unexplained weight loss
- Early detection is crucial for good prognosis in most cases and all patients must be encouraged to talk to their primary care physician about their symptoms.
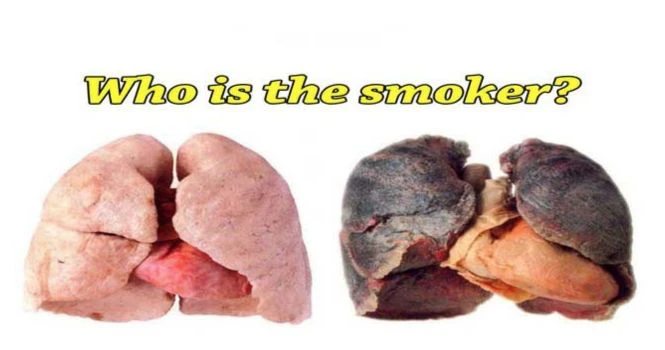
Smoking tobacco in any form is the major risk factor for lung cancer. Non smokers who breathe the smoke of others, often called secondhand smoke or passive smoking, are also at increased risk for lung cancer. Stopping exposure to tobacco smoke at any age lowers the risk of lung cancer.
Risk factors for lung cancer besides smoking include the following:
- Radon: An odourless radioactive gas produced naturally in rocks and soil, radon is found in homes and mines in some areas. Exposure to high indoor radon levels can cause damage to the lungs that may lead to cancer.
- Asbestos: If inhaled, asbestos particles can cause lung damage that may lead to lung cancer and mesothelioma (a rare cancer of the chest and abdominal lining).