Metformin is available as Metformin hydrochloride 500 mg tablets.This is a Prescription Drug. It has to be taken only on your doctor’s advice.
The remarkable feature is, it causes little or no hypoglycemia in non-diabetic or in diabetic patients. Hypoglycemia with metformin is rare. It is classified into the Biguanide class of oral Anti Diabetic drugs.
In the past, Guanidine containing extracts from Galega officinalis, the French lilac, were used for anti-diabetic , anti-hypertensive and anti-aging properties.
Phenformin, Buphormin and metformin were synthesized and were found to have blood sugar lowering properties accidently and approved for use in Europe in the 1950”s. Phenformin and Buphormin were banned and removed from the market as it caused lactic acidosis and led to many deaths.
Only Metformin was approved for use in 1995 by USFDA and used throughout the United States and the world, due to its less chances of lactic acidosis, which is a serious complication of the drug, though rare.
Metformin does not stimulate Beta cells in the pancreas. For Metformin to act, Insulin is required. It can only act in the presence of Insulin
Mechanism of Action of Metformin
Metformin actions are due to activation of AMP dependent Protein Kinase and key features are
- Suppresses Glucose output from the Liver
- Enhances Insulin mediated Glucose uptake by overcoming Insulin resistance in type 2 Diabetes
- Promotes Peripheral Glucose Utilization
- Retards intestional absorption of Glucose, Amino acids and Vitamin B12.
Metformin Side Effects
- Abdominal pain
- Anorexia
- Bloating
- Nausea
- Metallic Taste
- Mild diarrhea
- Tiredness
These are the usual complaints but are not serious, which tend to subside with time, in the majority of the patients.
Small increase in Blood Lactate occurs but lactic acidosis is rare. You must inform the medications which you are taking and your medical history, so that your doctor would advise and prescribe accordingly.
Vitamin B12 deficiency occurs as it impairs its absorption at higher doses
Contraindications of Metformin
Metformin is NOT to be given in patients with the following conditions,
- Kidney Diseases
90% of the drug is eliminated through the kidneys and any disease which decreases the filtration function of the kidneys, accuses accumulation of the drug, leading to toxicity and thereby lactic acidosis, which is a serious complication.
Metformin as we have seen inhibits the formation of Glucose from the liver by blocking pyruvate carboxylase, the enzyme which converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate, and thus leads to accumulation of lactic acid.
- Hypotensive states
- Heart failure
- Severe Respiratory/Hepatic disease
- Alcoholics
Metformin is used for
1. Diabetes Mellitus
- It is used to lower Blood Glucose levels and it can act only in presence of Insulin and not useful in Type 1 Diabetes where there is absolute lack of insulin.
It does not cause Hypoglycemia, even in patients who are non-diabetic.
- It doesn’t cause depletion or exhaustion of B Cells or beta cells in the pancreas
- Prevents complication of Diabetes
- HBA1c reduction by 0.8 to 1.2%
- Can prevent new onset type 2 Diabetes in obese middle ages with inplared glucose tolerance with Reduction of 25-31 % in incidence.
- Can be given with other diabetic drugs or injectable antidiabetic medication
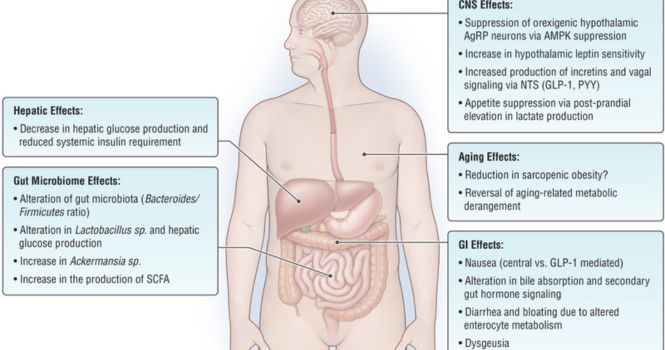
2. Weight Loss
It is not recommended as a standalone drug for Weight loss. But if the patient has evidence of prediabetes, and has insulin resistance and is not responding to lifestyle modifications, then in such conditions it is used.
It Promotes Weight Loss by suppressing appetite
Regulation of Obesity, Appetite and Weight Loss
3. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome PCOS
Insulin resistance and high insulin levels are the culprits in PCOS and treatment is aimed to tackle these first.
Metformin is found to improve and induce ovulation and fertility in patients with PCOS