The heart, which supplies blood to every part of the body, requires blood too.
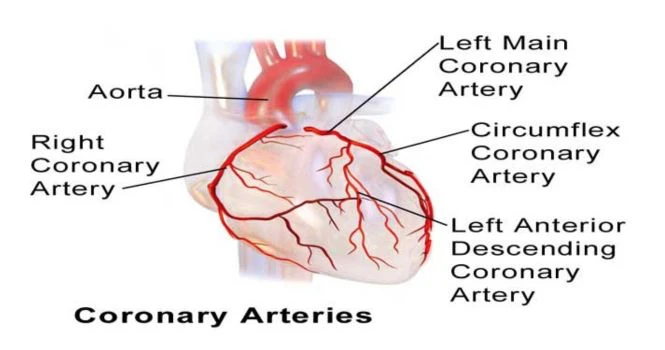
It is supplied by coronary arteries, which are branches of Aorta.
Aorta arises from the left ventricle.
Coronary Circulation: Coronary Arteries which supply Blood to the human heart:

Heart muscle is supplied by 2 Coronary arteries, Right coronary artery and Left coronary artery, both of which are the branches of the aorta. The arteries encircle the heart in a crown manner, hence named coronary arteries.
Right Coronary Artery
Right coronary artery supplies
i) Supplies the right ventricle
ii) Posterior portion of left ventricle
In 50% to 60% of humans, the right coronary artery is larger ( Right Dominant ) and supplies more blood to the heart than the left coronary artery.
The right coronary artery divides into the right posterior descending and large marginal branch.
Left Coronary Artery
i) Anterior and lateral parts of left ventricle
In 15% to 20% of humans, Left coronary artery is larger ( Left Dominant )
In 20% to 30% of individuals , both arteries supply an equal amount of blood.
The left coronary artery divides into the left anterior descending and circumflex artery.
Branches of Coronary Arteries
They divide and subdivide into smaller arteries which are called epicardiac arteries and further give rise to smaller branches called final arteries or intramural vessels.
Venous Drainage of the Heart
Venous drainage is by three type of vessels
- Coronary Sinus
- Anterior Coronary Veins
- Thebesian Veins
Coronary Sinus is the largest vein draining 75% of the total coronary flow. It drains from the left side of the heart and opens into the right atrium, near the tricuspid valve.
Anterior Coronary vein drains blood from the right side of the heart and opens directly into the right atrium.
Thebesian Veins drain deoxygenated blood from the myocardium into their respective chamber of the heart.
Factors regulating Coronary Blood Flow
Heart has the capacity to autoregulate its own blood supply and is not affected when the mean arterial pressure is between 60 mm to 150 mm of Hg.
Factors regulating coronary Blood Flow are
- Need for Oxygen
- Metabolic Factors
- Coronary perfusion pressure
- Nervous factors
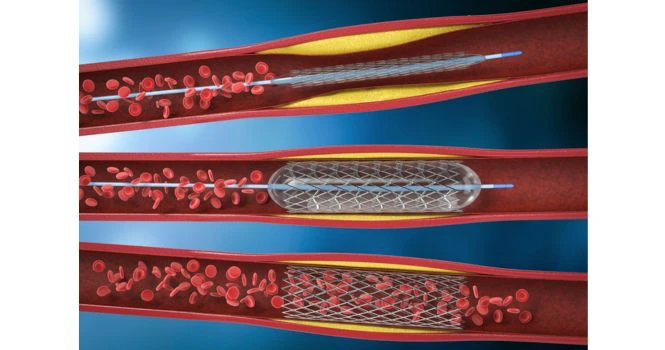
Coronary Artery Disease : Coronary Occlusion
Coronary arteries are end arteries.
If it gets blocked, then there is no other way the blood could reach other parts of the heart, beyond the block.
If there is a plaque (Fat, cholesterol, blood clot) blocking a coronary artery, then it would result in heart attack, which means, the areas supplied beyond the block undergo ischemic changes (Lack of oxygen supply lead to ischemic changes), which lead to death of portion of the heart.
The extent of damage to the heart depends on the degree of the block, which could be found out by Angiography.
The degree of block is expressed in percentage of blocked lumen (artery), if its 100% block then the blood cannot pass through it, while partial blocks allow a limited portion but still compromising the vital blood supply.